Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security protocol that requires multiple credentials for user authentication. MFA adds another layer of security to online accounts, making them less likely to be hacked or used for fraud. It requires two or more factors, such as passwords, biometrics, tokens, and more. MFA solutions can be changed to fit different needs, and they can help stop security breaches by making sure that no unauthorized users are given access to the system.
Why is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
Cybercriminals are always looking for ways to get into sensitive information without permission, so cybersecurity and data protection are very important. Single-factor authentication, or even two-factor authentication, which requires only one form of identification, such as a password, has many limitations. Passwords can be easily guessed or stolen, leaving user accounts vulnerable to attack.
MFA is increasingly important as cyberattacks become more sophisticated and frequent. By requiring users to provide both something they know (like a password) and something they have (like a smart card), multifactor authentication (and strong overall web authentication) greatly increases the security of user accounts and helps prevent data breaches.
What are the benefits of MFA?
When it's done right, multi-factor authentication lowers an organization's security risk, speeds up security response time, and helps stop attacks. It also makes sure that an organization is in compliance with industry or government rules.
Reduces security risk
MFA helps reduce the risk of identity theft and data breaches by making it harder for attackers to gain access to sensitive information. With MFA in place, even if one factor is compromised, there are still additional layers of protection that can help prevent unauthorized access. Using multi-factor authentication can make a big difference in an organization's security and protect it from possible threats.
Improves security response
One of the key benefits of multifactor authentication is that it improves security response times. If, for example, a hacker or other attacker tries to get in by using stolen credentials, multi-factor authentication can quickly spot the threat and send a message to security staff. This allows organizations to respond quickly and effectively to potential breaches, reducing the risk of data loss and other negative outcomes.
Prevention of data breaches and cyberattacks
Multi-factor authentication makes it much harder for hackers to get into sensitive data and systems by requiring more than one way to prove who you are. This can help prevent phishing attacks and other malicious activities. This can include everything from malware infections to social engineering attacks, which can be used to steal login information and gain unauthorized access to systems and data.
Compliance with industry regulations
MFA offers a number of benefits for both businesses and end-users. It can help increase user confidence and reduce fraud, as well as comply with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Multi-Factor Authentication Methods
The three main multi-factor authentication methods include knowledge-based authentication, physical authentication, and inherent authentication. Other forms of MFA include time- or location-based authentication and adaptive authentication. Using multifactor authentication can significantly increase the security of sensitive information and protect against unauthorized access.
Knowledge-based authentication
A knowledge-based authentication factor (KBA) requires users to answer a security question about their identity before gaining access. These questions can be based on personal information, such as an address or phone number, or knowledge-based information, such as a favorite color or a pet's name. KBA can be an effective way to verify a user's identity and prevent unauthorized access. However, it is important for users to choose strong and unique answers to these questions to ensure maximum security.
Physical authentication
For a physical authentication method to work, a user must be able to physically access a mobile device or a certain place. Examples of physical authentication methods include hardware tokens, smart cards, and biometric scanners.
Inherent authentication
Inherent authentication is a type of MFA method that verifies users based on their physical traits, like fingerprints or facial recognition. This method is very safe and hard to fake or get around, so it is a good way to keep sensitive information and systems from being hacked.
Time-based and location-based authentication
Time-based authentication involves using a code or one-time password (OTP) that is valid for a limited period of time, such as 15 minutes. On the user's device, an authentication app (like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator) will typically generate this code and send it to their mobile phone via SMS text message. Location-based authentication, on the other hand, considers a possession factor and uses the device's location to verify that it is in the same place as the user.
Adaptive authentication
Adaptive MFA looks at the user's behavior and environment, such as their location, the device they use, and their login history, to figure out how risky each login attempt is. Different authentication challenges may be given to the user as an extra security measure, depending on the level of risk that has been found. Adaptive authentication is popular in industries where sensitive information is constantly accessed and must be protected at all times.
Challenge Response Authentication
CRAM, short for Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism, is a powerful set of protocols designed to safeguard digital assets and services from malicious access. This authentication mechanism typically comprises two crucial elements—a challenge and a response—wherein a verifier poses a challenge to a user who is then required to provide the correct answer for successful authentication. The challenge-response protocols can range from a basic password to a dynamically generated request, making it a flexible authentication mechanism.
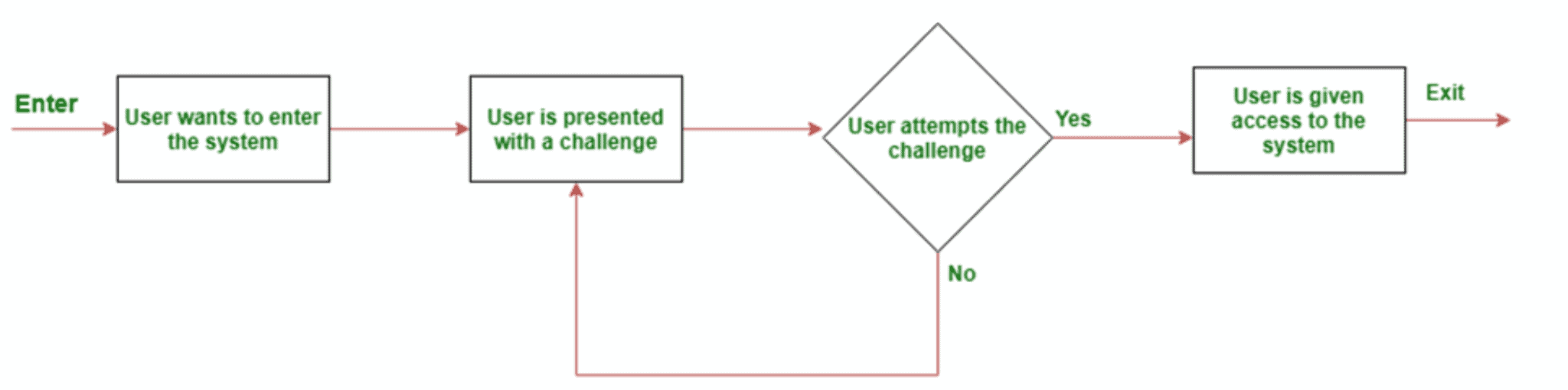
By implementing a challenge response authentication mechanism, businesses can effortlessly regulate access to confidential data and quickly detect any suspicious activities. With CRAM, companies have an easy-to-use security tool at their disposal that helps identify and weed out bad actors from their systems.
How to Implement MFA
An organization's IT team should make sure it has the necessary technical infrastructure in place to support MFA, including compatible hardware and software. Consider the different types of MFA authentication methods available and their associated costs. Also, keep user experience in mind when selecting a method. When the team decides on the MFA methods they'll use, organizations should educate their employees and users about best practices for maintaining security. To ensure maximum security, implement multi-factor authentication for all users, including administrators and privileged accounts. Adequate backups and recovery measures should be in place in case of system failures or errors. Here are a few of the common steps to setting up multi-factor authentication:
Create user Roles
Implementing multi-factor authentication requires a number of important steps, such as giving users permissions based on the roles they have been given. This makes sure that users can only get to the information and systems they need to do their jobs, which can help prevent security breaches.
In addition to user roles, it is also important to train users on the importance of using strong passwords and not sharing them with others. Multi-factor authentication can provide an extra layer of security, but it is still important for users to take basic security measures such as creating complex passwords and changing them regularly.
Create strong password policies
Creating a strong password policy is the first line of defense in multi-factor authentication. Strong passwords are hard to guess and have a mix of capital letters, numbers, and special characters. These should be required by password policies.
Rotate security credentials
By changing security credentials often, you can make sure that even if one factor is lost or stolen, like a password, there are still other ways to stop unauthorized access. In addition to rotating security credentials, it's also important for users to use different passwords for different services. This can help protect against credential stuffing attacks, in which attackers try to get into a user's other accounts by using their login information from one service that has been compromised.
Follow least privilege policy
Following the least privilege policy means that only users who need access to certain data or systems should be granted access. By limiting access in this way, you can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
MFA vs Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a type of security that requires a user to provide two pieces of evidence to prove who they are in order to access a system. The first is a password, and the second is usually a text message with a code sent to the user's phone. The second factor may also be the user's fingerprint, face, or retina.
While 2FA provides an extra layer of security, MFA takes security to the next level by adding more layers of verification. MFA is safer than 2FA because hackers are less likely to try to break into it. The biggest advantage of using MFA over 2FA is that it makes it extremely difficult for attackers to breach an account since they would need access to all the required credentials at once.
Limitations of Multi-Factor Authentication
While MFA provides an extra level of security, there are also some limitations associated with it. One is the cost and complexity of implementing multi-factor authentication systems. Another challenge is user experience, adoption, and awareness—many people may not understand why they need to go through the extra steps or may find the process inconvenient. Additionally, there can be issues with compatibility across different devices and platforms.
The most common way to deal with MFA challenges is to use cloud-based services that offer MFA as a service, which eliminates the need for companies to set up their own MFA infrastructure. Mobile-based MFA is becoming increasingly popular because it is convenient and easy to use.
Man-in-the-Middle Toolkits
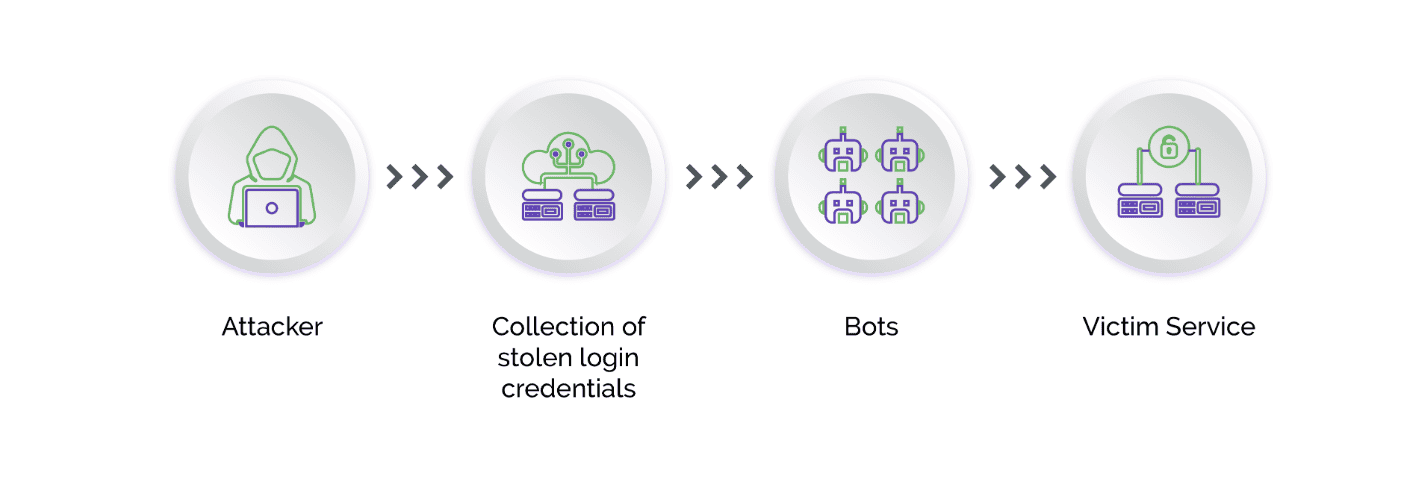
Another limitation of MFA is the fact that cybercriminals now use "phishing kits," which contain all the infrastructure needed for a phishing campaign, including automated tools, phishing scripts, templates for creating fake emails and websites, web servers, and storage used to collect credentials.
The latest evolution of phishing kits is the Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) toolkit, which acts as a malicious reverse proxy server of online services, mirroring target website contents to users while extracting credentials like MFA tokens and session cookies in transit. The MITM phishing kits also automate the harvesting of two-factor authenticated (2FA) sessions. In this way, criminals are able to trick both users and official websites, bypassing one-time passwords.
The best way to set up MFA is in conjunction with a robust bot management solution—like Arkose Labs—that can be configured on the website's login and registration workflows prior to the MFA step. The login or registration can be completed only if the web server receives the token issued by Arkose Matchkey, the strongest CAPTCHA challenge response in the business.
Conclusion
In conclusion, multi-factor authentication is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity and data protection. With the increasing number of cyberattacks and data breaches, it is essential to have additional layers of security beyond just passwords. MFA reduces security risks, improves security response, mitigates data breaches and cyber attacks, and ensures compliance with industry regulations. MFA can be set up in a number of ways, such as through knowledge-based authentication, physical authentication, inherent authentication, time- and location-based authentication, and adaptive authentication. Organizations need to create user roles, set up strong password policies, rotate security credentials, and follow the least privilege policy in order for MFA to work well. While there may be challenges when implementing MFA, such as user resistance or integration difficulties, they can be overcome with proper planning and training.
Also, it's important to use a bot management solution, like one from Arkose Labs, that can prevent, detect, and stop MITM attacks that can fool even the best multi-factor authentication.
Want to learn more? Book a demo today!