Phishing is a type of social engineering attack that aims to take advantage of the gullibility and/or naivety of legitimate system users. Phishing attacks can take different forms, such as email phishing, spear phishing, whaling, smishing (SMS phishing), and vishing (voice phishing).
According to Statista, in 2020, phishing emails were a leading point of entry for ransomware, constituting up to 54% of digital vulnerabilities. As a result, it's critical to recognize these attacks and take appropriate measures to stop them.
How do Phishing Attacks Work?
Most phishing attacks are delivered via email. Attackers go to great lengths to make their emails appear as authentic as possible. Most of the time, these emails send their intended victims to a phishing website, where bots deliver malware or steal users’ credentials.
Anatomy of a Phishing Email
Social engineering techniques are often used in phishing emails to trick the recipient into clicking on the link or downloading the attachment. This may include generic greetings, a sense of urgency, and requests for personal information.
Other red flags include strange URLs, spelling and grammar mistakes, and requests for personal information like account numbers. Emails that claim to be from IT departments, banks, government agencies, or other legitimate or "known" organizations are examples of phishing emails. These frequently imitate the domain names and frequently the "look" of well-known websites.

Phishing campaigns may have a subject line about an invoice that is past due, a purchase order, a request for information, shared files, or an IT notification. Fraudulent email messages about HR-related topics can be tricky because they frequently use a fake "HR" mailbox name and spoof the user's domain. Emails that look like they are from well-known online services, like Microsoft, are another source of fake business-related messages.
Techniques Used in Phishing Attacks
Cybercriminals use various techniques to accomplish their goals, including social engineering, link manipulation, and filter evasion. By understanding the techniques used in phishing attacks, you may be able to protect your business from this type of cybercrime.
Social engineering
Social engineering uses psychological tricks to trick people into giving out personal information or opening links and downloads that are harmful. Social engineering can involve pretending to be someone else, giving the target a false sense of urgency, or making threats to get them to reveal private information.
Link manipulation
Link manipulation involves sending an email or text message containing a malicious link that leads to a phishing website that appears legitimate but is actually designed to steal personal information from unsuspecting victims. Hackers often use shortened URLs to send people to malicious websites, and they may use domain spoofing to make their messages look like they came from a real company.
Filter evasion
Filter evasion involves using keywords and images to bypass email filters and spam blockers. This allows hackers to send phishing emails directly to victims' inboxes.
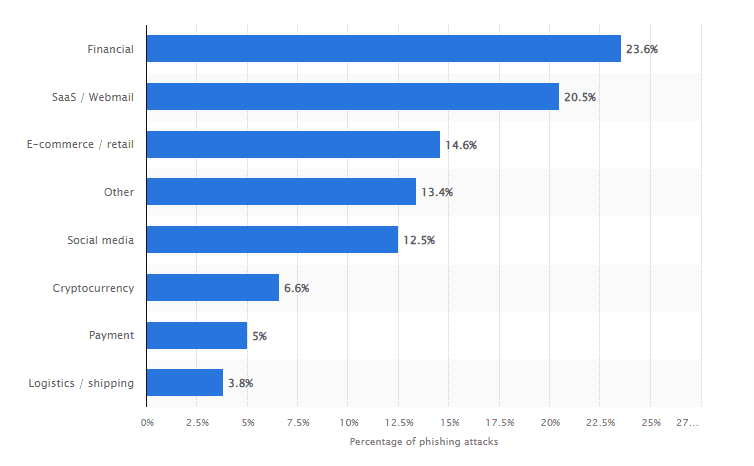
Online industries most targeted by phishing attacks as of Q1 2022
Common Types of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks may be generic scam emails sent to hundreds of thousands of email addresses or a very targeted phishing message directed at a particular person. In these personal attacks, the sender will write a personalized email that contains information that only a friend or coworker would know. Even the most cautious recipients may have a very difficult time avoiding becoming victims if the email is this kind. Here are some of the most common types of phishing attacks:
Email Phishing
Email phishing has been around since the 1990s. Typically, the email alerts the victim to the compromise of an account and requests that they respond immediately by clicking on a link. Most of the time, these emails are easy to spot because they have spelling or grammar mistakes.
Spear Phishing
Spear phishing attacks target a particular group or type of person, such as a system administrator or HR director. These emails may talk about the recipient's area of expertise, include a link to a file download that the victim is told to click, and demand a quick answer.
Whaling
Whaling is a type of phishing that is even more specific and tries to trick a "whale," like a CEO or CFO in a certain industry or company. The email may threaten the company with legal action, or mention "inside" financial information. Of course, the intended victim must click a link to "learn more" and is then directed to a fake website where they must enter login credentials and important company information, such as tax IDs and bank account numbers.
Smishing
Smishing is an attack that is carried out through cell phone text messaging or short message service (SMS). Smishing attacks often look like they come from a bank and come in the form of SMS messages. The text message informs the recipient that their account has been compromised and that they must act right away. The attacker questions the victim about their bank account number, SSN, etc. The attacker then has access to the victim's bank account.
Vishing
A vishing is carried out via phone call. A typical vishing attack involves a call from a person posing as a representative from a computer hardware, software, or antivirus company. They tell the victim that they have found a virus on the victim's computer. The attacker will then ask for credit card numbers so that the antivirus program on the computer can be updated. If successful, this type of attack is a double whammy: the attacker gets valid credit card information and may also have installed malware on the victim's computer. The malware might include anything from a bot to a Trojan that spies on the victim's online behavior in order to steal more information, such as bank account credentials.
Man-in-the-Middle
The latest evolution of phishing attacks is the Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) toolkit, which acts as malicious reverse proxy servers of online services, mirroring target website content to users while extracting credentials like MFA tokens and session cookies in transit.
Impact of Phishing Attacks
According to the FBI Internet Crime Report 2021, phishing was the fastest growing type of internet crime from 2019 to 2021, and bad actors continue to evolve their phishing attack techniques. These attacks can have severe consequences, as phishing is the fourth most common and second most expensive cause of data breaches, costing businesses an average of USD 4.65 million per incident.
When a company loses private or sensitive information because of a phishing attack, it does a lot of damage to its reputation and credibility. If ransomware is injected into a system through a phishing attack, the financial losses can be devastating to a business. Costs include direct losses from stolen funds as well as indirect costs such as time spent recovering from the attack. Businesses could experience disruptions in their operations or a decline in market share.
Preventing Phishing Attacks
One way to stop phishing attacks is to use a full-scale security plan that includes educating users. By teaching people how to spot and avoid phishing emails in their inbox, you can make it much less likely that an attack will succeed. Strong authentication measures, like two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA), which require users to show more than one form of identification before they can access sensitive data, are another effective strategy.
It's also important to keep an eye on the IT environment for signs of suspicious activity, like logins from people you don't know or network traffic that seems out of the ordinary. This can help you quickly identify and respond to potential attacks before they can cause significant damage. Regularly updating system software and patches and using a bot management solution can also protect against vulnerabilities that attackers may try to exploit.
Educating Yourself and Your Employees
The first step in preventing phishing attacks is educating yourself and your employees on the dangers of phishing attacks and how to recognize them. Be aware of suspicious emails, website links, and attachments that could be malicious. It's also important to have strong password policies in place and use multi-factor authentication whenever possible.
Multi-factor Authentication
MFA) asks users to prove who they are with two or more pieces of information, like a password, email address, phone number, or biometric data. This additional layer of security makes it more difficult for hackers to gain access to your accounts. In theory, MFA also ensures that even if a user's credentials are stolen during a phishing scam, the hacker won't be able to access the account without additional verification. But, in practice, scammers can now use Man-in-the-Middle attacks to circumvent MFA.
Security Solutions and Tools
Another critical step is regular backup of data, so that if you do become the victim of a phishing attack, you can recover quickly. To protect against phishing attacks, organizations should also use security tools like a firewall and anti-spam filters. Most importantly, businesses need a holistic cybersecurity plan that includes a robust bot management solution—like Arkose Labs—that can detect phishing attacks and stop them before damage is done.
The Arkose Labs’ platform combines transparent detection with targeted attack response to catch fraud early in the customer journey without impacting good users. It is set up before the MFA step in a website's login and registration workflows. The login or registration workflow can be completed provided the web server receives the token issued by the Arkose Platform upon successful completion of the detection and adaptive challenge response processes.
Conclusion
Phishing attacks are a growing threat, and it's important to understand how they work and the impact they can have. Attackers can get people to give them sensitive information or download malware by using techniques like social engineering, link manipulation, and filter evasion. Common types of phishing attacks include SMS phishing, voice phishing, spear phishing, whaling, social media phishing, and more. If you fall for a phishing attack, you could lose your data, have your identity stolen, or lose money. Preventing these attacks requires education and security solutions. Take action now to protect yourself and your business from these dangerous threats.
Want to learn more? Book a demo today!