The Digital Environment
Today's financial services landscape evolves quickly as a result of groundbreaking technology and an unwavering commitment to convenience, but this progress comes at a cost—an increase in cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Both fintechs and traditional banks face significant challenges in this digital environment, emphasizing the need for a proactive security and bot management approach. This approach aims to protect against breaches while maximizing the advantages of digital transformation.
As institutions navigate this intricate landscape, they adopt digital transformation to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. However, this journey comes with potential risks, demanding a careful grasp of the threat environment.
This interactive ebook, "Charting Cyber Threats in Finance,” serves as a strategic compass for industry leaders, decision-makers, and security professionals. Its core objective is to offer comprehensive insights into the multifaceted challenges that underpin the critical use cases in today's financial services landscape. By delving into the diverse dimensions of cyber threats specific to fintechs and banks, this resource arms stakeholders with the knowledge and strategies they need to secure sensitive data, adhere to regulatory standards, and ensure the seamless flow of commerce and revenue.
Integral to this conversation is the critical role of security, privacy, and compliance. These threads intricately weave together to form the foundation of informed decision-making. When kept in balance, trust emerges as a defining factor within the financial services ecosystem—a principle encapsulated by the notion that trust is established through the fulfillment of commitments and promises.
It is undeniable that the financial services sector remains a prime target for cybercriminals, drawn by the allure of potential financial gains. Even as institutions invest in robust security measures, cybercriminals persistently devise innovative methods to infiltrate. Our examination of this persistent challenge uncovers not only the motives behind these breaches but also sheds light on the top use cases in the industry and how they can be remedied through best practices.
The Need for Security and Bot Management
In modern financial services, which includes both traditional banks and fintech firms, the imperative for cybersecurity and effective bot management has never been more crucial. As the industry continues to rapidly adopt digital platforms and services, it becomes a prime target for cybercriminals seeking to exploit the vast amounts of sensitive data and financial assets in their possession. This underscores the pressing need for robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard the integrity, privacy, and trust that are paramount to financial transactions.
Within the realm of fintech startups and established banks, the proliferation of digital transactions and online financial services has opened up new avenues for malicious bot attacks and other cyber threats. These threats range from intricate phishing schemes aimed at unsuspecting customers to large-scale data breaches that can disrupt entire financial ecosystems. Recognizing these evolving tactics sheds light on the significance of implementing comprehensive security strategies.
Additionally, the emergence of malicious bot attacks has introduced a growing concern across the financial services landscape. These automated bots can engage in activities such as unauthorized fund transfers, fraudulent account creation, and even manipulation of stock prices. To counter this multifaceted threat, proactive bot management strategies are becoming essential. Incorporating advanced technologies like machine learning and behavioral analytics allows for the detection and mitigation of various bot-driven risks.
In a context where innovation is intertwined with risk, decision-makers within the financial sector are increasingly compelled to prioritize cybersecurity and bot management. By understanding the nuanced challenges presented by these threats, stakeholders are better equipped to reinforce their defenses, adapt to evolving attack methods, and ultimately ensure the secure foundation that enables trustworthy financial interactions within our interconnected world.
Cyber Threats in Finance
In the dynamic arena of online finance, the digital landscape offers both convenience and innovation alongside a growing array of challenges. Account compromise, new account fraud, and unauthorized use now stand as the top three cyber threats facing financial businesses and banks today. As these services continue to embrace the digital age, a clear focus on understanding and mitigating these risks emerges as a pivotal aspect of strategic planning. This comprehensive approach is essential to maintain the delicate balance between providing seamless customer experiences and fortifying the security measures needed to safeguard financial integrity.
Account compromise refers to a situation in which unauthorized individuals or entities gain access to a user's or customer's account within a system or platform, typically for malicious purposes. This unauthorized access can occur in various ways, such as through phishing, bot attacks, malware infections, or exploiting vulnerabilities in software or security protocols.
Account compromise has far-reaching consequences for financial services operating in the digital sphere. This threat undermines the essential pillars of security, trust, and operational stability that underpin online banking. Its effects extend beyond financial losses, creating a series of challenges that reverberate across the industry.
What are the top use cases associated with account compromise?
Account Takeover (ATO) in the context of financial services refers to the unauthorized access and control of a user's account by cybercriminals. During an ATO attack, the attacker gains access to a legitimate user's account credentials, often through methods like phishing, credential stuffing, or social engineering. Once they have control of the account, they can exploit it for various malicious purposes, such as making unauthorized transactions, transferring funds, changing account settings, or even stealing personal and financial information.
Signs of an ATO attack in finance include:

Unusual account activity

Multiple failed login attempts

Account lockouts

Unrecognized devices or locations

Changes in account information

Unusual Communication

Disruption of Service

Unexplained email alert

Unwanted Transaction

Increased Spam and/or phishing attacks
Impostor scams thrive when hackers gain unauthorized access through ATO fraud. This links closely with identity theft, where hackers pretend to be someone else to create a new account. In 2022, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) got over 725,000 reports of impostor scams, where criminals posed as someone else to steal money or info. Although this was fewer than the almost one million reports in 2021, the money lost to impostor scams hit a record high: $2.67 million in 2022, up from $2.4 million in 2021.
What are the top five best practices for beating ATO attacks?
1
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Implement robust MFA across your platform to require users to provide multiple forms of authentication before accessing their accounts. This could involve a combination of something they know (password), something they have (mobile device or hardware token), and something they are (biometric verification). MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
2
Continuous Monitoring and User Behaviour Analytics (UBA)
Employ advanced monitoring tools and user behavior analytics to detect anomalies and unusual activities in real-time. By analyzing user behavior patterns, you can promptly identify suspicious actions and respond swiftly to potential ATO attempts.
3
Risk-Based Authentication
Utilize risk-based authentication to assess the risk level of each login attempt based on factors such as device, location, IP address, and user behavior. Adjust the level of authentication required accordingly, ensuring that high-risk attempts undergo more stringent verification.
4
Regular User Education
Conduct ongoing user education and awareness campaigns to educate your users about ATO threats, phishing risks, and best practices for maintaining strong passwords. Encourage them to adopt secure behaviors and promptly report any suspicious activity.
5
Incident Response Plan and Testing
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines procedures for identifying, mitigating, and recovering from ATO incidents. Regularly test and update this plan to ensure its effectiveness in addressing evolving threats. Conduct simulated ATO attacks to assess the readiness of your security measures and response protocols.
Credential Stuffing is a rampant cyber threat in which cybercriminals exploit compromised login credentials, often acquired from previous data breaches, to gain unauthorized access to user accounts across various online platforms. This technique relies on the common practice of reusing passwords across multiple accounts, making it a particularly effective method for fraudsters to breach systems and compromise user information.
Signs of an Credential Stuffing in finance include:

Unusual account activity

Account lockouts

Spike in failed logins

Unfamiliar transactions

Unsuccessful login notification

Access from new devices

Unexplained password resets

Unusual activity post-logins

Increase in customer support requests
The year 2022 witnessed the emergence of the largest credential stuffing attacks on record, signifying a notable shift in the landscape. Analysis of the data reveals a significant trend: these attacks contribute to approximately 34% of all traffic and authentication events on a website. Within this context, a distinctive pattern comes to light. While most industries experience a credential stuffing rate below 10% for login attempts, certain sectors stand out. Notably, financial services encounter these attacks as the predominant source of login activity.
The consequences of credential stuffing are far-reaching. Successful attacks can lead to unauthorized access to bank accounts, fraudulent transactions, identity theft, and reputational damage for financial institutions. As the financial sector continues to digitize and offer online services, the risk of credential stuffing becomes more pronounced.
What are the top five best practices for beating credential stuffing attacks?
1
Password Policies and Complexity Requirements
Enforce strong password policies that require users to create complex passwords with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Implement password length and expiration rules to discourage the use of easily guessable or common passwords.
2
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords. Require users to provide additional authentication factors, such as a one-time code sent to their mobile device or biometric verification, before accessing their accounts.
3
Credential Monitoring and Dark Web Scanning
Regularly monitor for compromised credentials on the dark web and other illicit online marketplaces. Implement credential monitoring services to detect if user credentials have been exposed in data breaches, allowing you to prompt affected users to update their passwords.
4
Rate Limiting and Account Lockouts
Implement rate limiting on login attempts to restrict the number of unsuccessful login tries within a certain time frame. Implement temporary account lockouts after a specified number of failed attempts to deter automated credential stuffing attacks.
5
User Education and Awareness
Educate your users about the risks of credential stuffing attacks and the importance of using unique passwords for each online account. Encourage them to regularly update their passwords and avoid reusing passwords across multiple platforms.
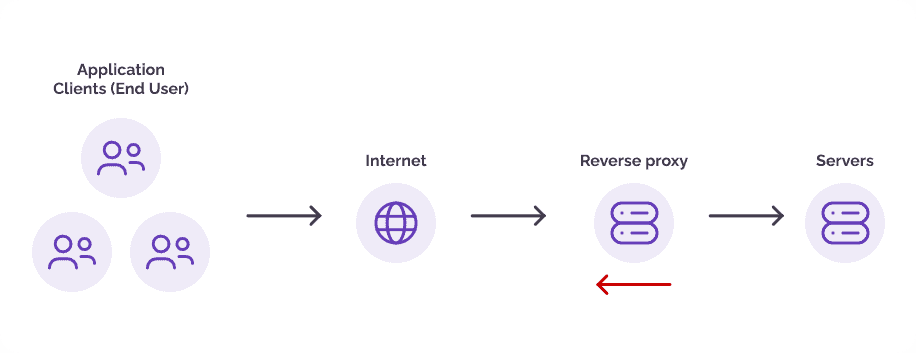
Reverse proxy attacks occur when attackers target the communication channel between clients and a server, often leveraging a compromised or malicious reverse proxy server to intercept, alter, or steal sensitive data. This form of attack exploits vulnerabilities in the reverse proxy infrastructure, allowing malicious actors to manipulate user requests, inject malicious code, or gain unauthorized access to confidential information.
Signs of an Reverse proxy attacks in finance include:

Unusual network activity

Unexpected data modification

Incomplete or slow transactions

Abnormal browser behavior

Authentication anomalies

Unexplained requests for sensitive information

Unusual account activity

Device or location changes

Security certificate warnings
Lately, a surge has been observed in the utilization of reverse proxies by malicious entities to orchestrate Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks. This trend is being propelled by an emerging platform named EvilProxy. In contrast to conventional phishing tactics that rely on a static replica of a well-known website, threat actors now exploit reverse proxy techniques, introducing a notably more perilous dimension.
In an alarming twist, even less experienced attackers can readily initiate campaigns, requiring only a few simple maneuvers and scant knowledge of reverse proxy intricacies. The not-so-underground industry of cybercrime-as-a-service (CaaS) makes this effort far easier than it should be. The aftermath of such campaigns can result in the wholesale pilferage of crucial credentials and cookies, posing a heightened risk to cybersecurity.
What are the top five best practices for beating reverse proxy attacks?
1
Implement Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Deploy a robust WAF that can detect and block malicious traffic, including requests originating from compromised reverse proxies. Configure the WAF to monitor incoming traffic patterns and identify anomalies indicative of reverse proxy attacks.
2
Check Code Integrity
Businesses can effectively counter reverse proxy attacks by leveraging client-side JavaScript techniques. Employ integrity checks using checksums or hashes to validate the integrity of crucial files. Generate unique tokens with JavaScript for each session, thwarting replay attacks. Detect abnormal behavior through behavioral analysis of user interactions. Implement a Content Security Policy (CSP) to restrict script sources and enhance client-side security.
Employ a Web Application Firewall (WAF) alongside real-time monitoring for timely threat response. Additionally, implement strict input validation and data sanitization practices to counter malicious script injection attempts through the reverse proxy. Regular code reviews and updates are essential to ensuring proper input validation before processing, further bolstering defenses against these attacks
3
Use Secure Communications
Employ encryption protocols, such as HTTPS, to secure communications between the reverse proxy and your backend servers. Ensure proper configuration of SSL/TLS certificates and regularly update them to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
4
IP Whitelisting and Rate Limiting
Implement IP whitelisting to restrict access to your backend servers only from trusted sources, preventing unauthorized use of reverse proxies. Additionally, enforce rate limiting on incoming requests to prevent overwhelming your servers with malicious traffic.
5
Regular Monitoring and Log Analysis
Continuously monitor incoming traffic and logs for unusual patterns or signs of suspicious activity. Implement robust logging mechanisms that capture relevant information about incoming requests, allowing for timely detection and response to reverse proxy attacks.
This sophisticated form of identity manipulation has swiftly gained prominence as a formidable challenge for fintechs and digital banks. In this malicious scheme, bad actors exploit gaps in verification processes and leverage stolen or entirely fictitious identities to establish fraudulent accounts. The allure of seamless digital onboarding and the potential for quick financial gains make fintechs and digital banks particularly attractive targets.
As these innovative institutions strive to provide convenient and accessible financial solutions, they concurrently grapple with the intricate task of differentiating genuine customers from fraudulent ones. The surge in new account fraud underscores the pressing need for these financial entities to bolster their security measures, enhance identity verification protocols, and remain vigilant.
What are the top use cases associated with new account fraud?
Synthetic identity fraud is a type of cybercrime where attackers create fictitious identities or combine real and fabricated information to establish fraudulent accounts. These synthetic identities are then exploited to apply for loans, credit cards, or other financial services, with the ultimate goal of conducting bogus transactions or accessing funds.
According to a Federal Reserve Payments Study in 2022, synthetic identity fraud accounts for a substantial portion of losses in the U.S. payments system. This type of fraud often goes undetected for an extended period, as criminals meticulously build the synthetic identities over time, making it difficult for traditional verification methods to spot the deception.
Signs of synthetic fraud in finance include:

Unusual account activity

Inconsistent identification

Rapid credit building

Uncommon credit usage

Excessive credit inquiries

Multiple payment methods

Mismatched personal data

Similar data across accounts

Pattern of defaults

Unusual geographic behavior
The impact of synthetic fraud on the financial sector is multifaceted. Financial institutions face financial losses, reputation damage, and regulatory compliance challenges as they grapple with identifying and addressing fake accounts. Moreover, legitimate customers might experience delays or difficulties due to enhanced identity verification measures put in place to combat synthetic fraud.
What are the top five best practices for beating Synthetic fraud?
1
Identity Proofing
Implement robust identity verification processes during account creation and transactional activities. Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometric authentication, and document validation to ensure the legitimacy of user identities.
2
Behavioural Analytics
Leverage user behavior analytics to detect unusual patterns and anomalies in user activities. Monitor for deviations from established behavior to identify potential synthetic accounts or fraudulent activities.
3
Data Validation and Authentication
Validate user-provided data against authoritative sources to ensure accuracy. Authenticate user information such as addresses, phone numbers, and social security numbers to prevent the creation of synthetic identities.
4
Collaborative Data Sharing
Collaborate with industry partners and data sharing networks to identify and flag known instances of synthetic fraud. Sharing information about fraudulent identities and patterns can help prevent their use across multiple platforms.
5
Machine Learning and AI
Utilize advanced machine learning and AI algorithms to detect patterns indicative of synthetic fraud. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data and identify hidden correlations that may indicate fraudulent activities.
Application fraud refers to the deceptive practice of submitting falsified or misleading information when applying for financial products or services, such as loans, credit cards, or insurance policies. This type of fraud aims to exploit vulnerabilities in the application process to gain access to funds or benefits that the fraudster is not entitled to. Fraudsters often manipulate or fabricate personal details, income information, or employment history to secure approvals for financial products, thereby evading traditional identity verification methods.
Signs of an Application fraud in finance include:

Inconsistent information

Unverifiable references

Unusual credit requests

Suspicious documentation

Excessive income claims

Frequently changing personal information

Abnormal spending patterns

High-risk industries

Unauthorized access attempts

Unfamiliar IP addresses
In addition to the impact on businesses, legitimate customers may also experience delayed approvals or heightened scrutiny due to enhanced verification measures aimed at thwarting application fraud.
What are the top five best practices for beating application fraud?
1
Robust Identity Verification
Implement strong identity verification processes during the application process. Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA), document validation, and biometric verification to ensure the authenticity of applicants’ identities.
2
Bot & Fraud Detection Tools
Utilize advanced fraud detection tools and technologies that can analyze application data in real-time. Employ machine learning algorithms to detect patterns and anomalies indicative of fraudulent activities.
3
Data Validation and Enrichment
Validate and enrich applicant-provided data using authoritative sources. Verify addresses, phone numbers, and other personal information to ensure accuracy and legitimacy.
4
Document Verification
Implement document verification processes to authenticate identity documents, such as driver’s licenses or passports, provided during the application process. This helps prevent the use of fake or tampered documents.
5
Behavioral Analysis
Monitor applicant behavior and interactions with your platform. Analyze user behavior patterns to detect inconsistencies or suspicious activities that may indicate application fraud.
Promo abuse fraud involves the misuse or exploitation of promotional offers, discounts, or incentives provided by financial institutions or businesses. Fraudsters exploit these offers to gain unwarranted benefits, such as obtaining credit card rewards, sign-up bonuses, or cashback offers through fraudulent means.
Signs of an Promo abuse fraud in finance include:

Multiple redemptions of same promotion

Excessive account creation

Highly unusual behavior patterns

Massive influx of account registrations

Unauthorized sharing of promotions

Overlapping or unusually coordinated transactions

Unexplained account activity

Stolen or fabricated information

Automated scripting

Attempts to circumvent promotional restrictions
Financial institutions incur financial losses due to providing rewards or benefits to fraudulent accounts, and legitimate customers may experience reduced availability of promotions or increased scrutiny in accessing promotional offers. The impact of promo abuse fraud extends beyond immediate financial losses. It can erode customer trust, damage the reputation of financial institutions, and lead to regulatory compliance issues. Furthermore, the diversion of resources to combat promo abuse fraud detracts from other critical cybersecurity and fraud prevention initiatives.
What are the top five best practices for beating promo abuse fraud?
1
Clear Terms and Conditions
Clearly define and communicate the terms and conditions of your promotions. Ensure that users understand the rules, eligibility criteria, and limitations of the offer to discourage fraudulent attempts.
2
Limit Usage
Implement restrictions on the number of times a promotional code or offer can be used by a single user. Set usage limits per account, device, or IP address to prevent excessive and abusive redemption.
3
Verification Mechanisms
Incorporate verification mechanisms to ensure that users meet the eligibility criteria for the promotion. Utilize identity verification, document validation, or other methods to confirm user authenticity.
4
Behavioral Analytics
Monitor user behavior and interactions with your platform to detect unusual patterns or anomalies associated with promo abuse. Analyze user activities to identify potential fraudulent activities.
5
Monitoring and Reporting
Continuously monitor promo code usage and track suspicious activities. Implement reporting mechanisms that allow users to flag or report suspicious behavior, enabling timely intervention.
Unauthorized use, a concerning phenomenon involving unauthorized access to confidential financial accounts and services, has emerged as a critical challenge within the realm of fintechs and digital banks. This worrisome trend encompasses unauthorized access to sensitive financial accounts and services, exposing these innovative institutions to a heightened risk of data breaches, financial fraud, and reputational damage. As fintechs and digital banks redefine the way financial transactions are conducted, their digital platforms become prime targets for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in the pursuit of illicit gains.
Unauthorized use not only jeopardizes the security and confidentiality of customer information but also poses substantial operational and regulatory challenges. The need for these institutions to effectively combat unauthorized access through robust security protocols, advanced authentication mechanisms, and vigilant monitoring has become an urgent imperative to ensure the continued trust of their clients and the integrity of their services.
What are the top use cases associated with unauthorised use?
SMS toll fraud, also known as SMS pumping or IRSF, is a type of cyberattack where fraudsters manipulate or exploit Short Message Service (SMS) messages to initiate unauthorized premium-rate charges to a mobile phone account. This type of fraud often involves sending deceptive messages that prompt recipients to unknowingly subscribe to premium services, make micropayments, or engage in interactions that result in financial losses.
Signs of an SMS toll fraud in finance include:

Unsolicited messages

Unexpected charges

Premium service notification

Texts with deceptive links

Continuous message flow of instructions

Impersonation of financial institutions

Unknown short codes

Unfamiliar message content

Excessive message frequency
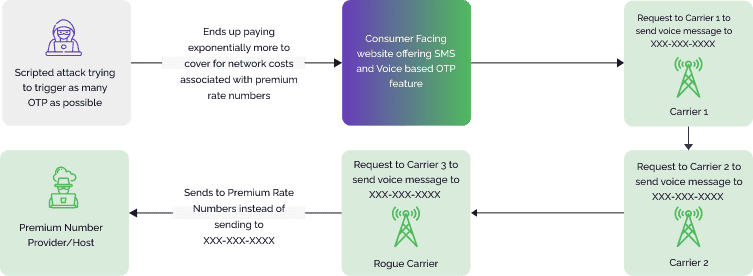
The impact of SMS toll fraud on the financial sector is two-fold. Consumers may experience unexpected charges on their mobile bills, leading to financial stress and potential disputes with mobile service providers. Financial institutions also face challenges in safeguarding their customers' accounts and maintaining trust in their services. These fraudulent and expensive SMS transactions can net fraudsters and rogue telecom operators a per-message payout of $1 or more. One recent study showed that SMS toll fraud cost a collective $10 billion in 2021, up from $1.8 billion in years past.
What are the top five best practices for beating SMS toll fraud?
1
Advanced Bot detection Tools
Invest in advanced bot detection solutions specifically designed for the finance industry. These tools utilize machine learning and behavior analysis to distinguish between legitimate user interactions and fraudulent bot activities.
2
Behavioural Analytics
Implement behavioral analysis techniques that can identify abnormal patterns of interaction. Legitimate users exhibit certain behavioral characteristics that bots usually lack, enabling your system to differentiate between the two.
3
Device Fingerprinting
Utilize device fingerprinting to track and identify devices used for transactions. Bots often use multiple devices, IPs, and locations rapidly, while legitimate users have consistent patterns.
4
CAPTCHA and Challenge-Response
Integrate CAPTCHA or challenge-response mechanisms as additional layers of security. These tools can effectively distinguish between human users and automated bots by requiring actions that are challenging for bots to replicate.
5
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Implement real-time monitoring of your systems and adapt your bot prevention strategy as threats evolve. Regularly update your bot detection solutions to stay ahead of new and sophisticated fraud tactics.
API abuse refers to the malicious exploitation of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) – the interfaces that allow different software applications to communicate and interact. In the context of the financial sector, API abuse involves unauthorized access, manipulation, or misuse of APIs to compromise security, steal sensitive data, initiate fraudulent transactions, or disrupt services.
Signs of an API abuse in finance include:

Unusual transaction patterns

Excessive API call from user or IP address

Unauthorized data access

Rapid credential testing

Unexplained account modifications

Geographic anomalies

Abnormal data flows

Suspicious user behavior

Mass data export

Exceeded rate limits for API use
The consequences of API abuse for the financial sector are far-reaching. Financial institutions face data breaches, financial losses, regulatory non-compliance, and reputational damage. Furthermore, customers' trust in online banking and financial services may be eroded, leading to potential customer attrition.
What are the top five best practices for beating API abuse?
1
Authentication and Authorization
Implement strong authentication mechanisms for API access, such as API keys, OAuth tokens, or JWT tokens. Ensure that only authorized users and applications can access your APIs, and enforce granular access controls based on roles and permissions.
2
Rate Limiting and Throttling
Set rate limits and throttling mechanisms to restrict the number of API requests that can be made within a certain time period. This prevents excessive requests from overwhelming your APIs and helps deter abusive behavior.
3
Input Validation and Sanitization
Implement rigorous input validation and data sanitization to prevent injection attacks and malicious payloads. Validate and sanitize all user inputs and parameters to prevent unauthorized access or data manipulation.
4
API Monitoring and Analytics
Continuously monitor API traffic and analyze usage patterns to identify unusual or suspicious activities. Implement real-time alerts and anomaly detection mechanisms to promptly detect and respond to potential API abuse. Organizations can enhance API abuse protection with a Web Application Firewall (WAF) and bot manager. These tools monitor usage for anomalies, thwarting malicious patterns. WAF analyzes incoming requests, while the bot manager distinguishes real users from bad bots. This strategy safeguards against unauthorized API access, data scraping, and maintains data integrity, adapting to evolving threats through continuous monitoring and adjustment.
5
API Security Testing
Regularly conduct security assessments and penetration testing on your APIs to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Address any discovered issues promptly and ensure that your APIs are robustly secured against common attack vectors.
Scraping refers to the automated extraction of data from websites, applications, or databases. Cybercriminals use scraping techniques to gather valuable information, such as stock prices, market data, account details, or customer information, for malicious purposes. This unauthorized data collection can lead to security breaches, fraud, and other detrimental outcomes. Financial institutions are vulnerable to scraping attacks, as cybercriminals aim to exploit vulnerabilities in web interfaces, APIs, or mobile apps to access sensitive financial data.
Signs of an Scraping in finance include:

Unusual traffic patterns

Excessive requests from a single IP address

Consistent data discrepancies

Patterned access

Rapid or repetitive searches

Increased load on servers

Unexplained creation of user accounts

Anomalies in user behavior

Data consistency issues

Unauthorized API access
The impact of scraping on the financial sector is profound. It can lead to compromised customer data, unauthorized access to accounts, fraudulent transactions, and even market manipulation. Additionally, scraping attacks can undermine customer trust, damage a financial institution’s reputation, and result in regulatory and legal consequences.
What are the top five best practices for beating Scraping?
1
Robust Access Controls
Implement strong access controls and authentication mechanisms to restrict access to sensitive data and resources. Utilize technologies like CAPTCHA, API keys, and rate limiting to differentiate between legitimate users and malicious scrapers.
2
Content Protection Techniques
Utilize techniques such as obfuscation, tokenization, and dynamic content rendering to make it difficult for scrapers to extract data from your website. Protect valuable information by structuring it in ways that are challenging for automated scraping tools to interpret.
3
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Deploy a WAF that can detect and block scraping attempts. Configure the WAF to monitor incoming traffic for patterns indicative of scraping activities and automatically block or redirect suspicious requests.
4
Monitoring and Analytics
Continuously monitor your website’s traffic and analyze patterns to detect sudden spikes in activity that could indicate scraping. Implement real-time alerts and anomaly detection mechanisms to promptly identify and respond to scraping attempts.
5
Legal Measures
Establish and communicate clear terms of use that explicitly prohibit scraping activities without authorization. Consider using legal tools such as cease and desist notices or legal actions against persistent scrapers who disregard your terms.
Arkose Labs for Finance
Arkose Labs offers comprehensive solutions to empower online businesses in the financial sector to effectively combat a wide range of cyber threats, including the top use cases explored in this paper. By harnessing innovative technologies and a holistic approach, Arkose Labs enables financial institutions to safeguard their platforms, data, and user experiences from malicious actors and bots.
Arkose Labs Solutions
In the battle against ATO attacks and credential stuffing, our challenge puzzle known as Arkose MatchKey provides advanced behavioral analytics and machine learning algorithms that analyze user behavior patterns. By detecting unusual or suspicious activities, we help financial businesses identify and thwart fraudulent login attempts, ensuring the security of user accounts and preventing unauthorized access.
Reverse proxy attacks, which exploit vulnerabilities in the infrastructure, are a significant concern for the financial sector. The real-time threat detection and protection mechanisms of Arkose Bot Manager not only detect reverse proxy attacks but also effectively counteract them. By identifying and blocking malicious reverse proxy traffic, Arkose Labs safeguards financial institutions from data breaches and unauthorized access.
As we know, promo abuse fraud, SMS toll fraud, API abuse, and scraping are also rampant in the financial sector. Arkose Labs employs the combination of Arkose Bot Manager with the CAPTCHA-based challenges and behavioral analysis of MatchKey, to thwart malicious activities across various touchpoints. By continuously monitoring interactions and deploying real-time defenses, we help financial institutions maintain the integrity of their services and protect user data.
For synthetic fraud and application fraud, both of which pose significant challenges for financial businesses, we leverage our proprietary technology to differentiate between genuine users and synthetic identities. Through intelligent risk assessment and adaptive authentication, Arkose Labs ensures that only legitimate users gain access, thereby preventing fraudulent applications and transactions.
Arkose Labs empowers online businesses in the financial sector to combat the top use cases prevalent in the industry. Through cutting-edge technology, adaptive authentication, and real-time threat detection, our technology enables financial institutions to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, ensuring a secure and trusted digital environment for their customers and stakeholders.