What is digital fraud?
Fraudulent activities conducted using digital means for financial gain are called digital fraud. Digital fraud causes financial loss, exposure of sensitive data, brand abuse and loss of trust among consumers and other stakeholders.
Fighting off digital fraud is a continuous battle for businesses and consumers alike. The integration of advanced technology has led to the emergence of sophisticated methods of deception, including the use of bots. These automated programs can mimic human behavior to bypass security measures, engage in large-scale attacks like phishing and credential stuffing, and manipulate systems for fraudulent purposes. By exploiting vulnerabilities in digital platforms, bots can execute high-speed transactions and steal information, exacerbating the impact and scale of digital fraud.
Types of digital fraud
Attackers exploit technology in a number of ways to execute digital fraud, as explained below:
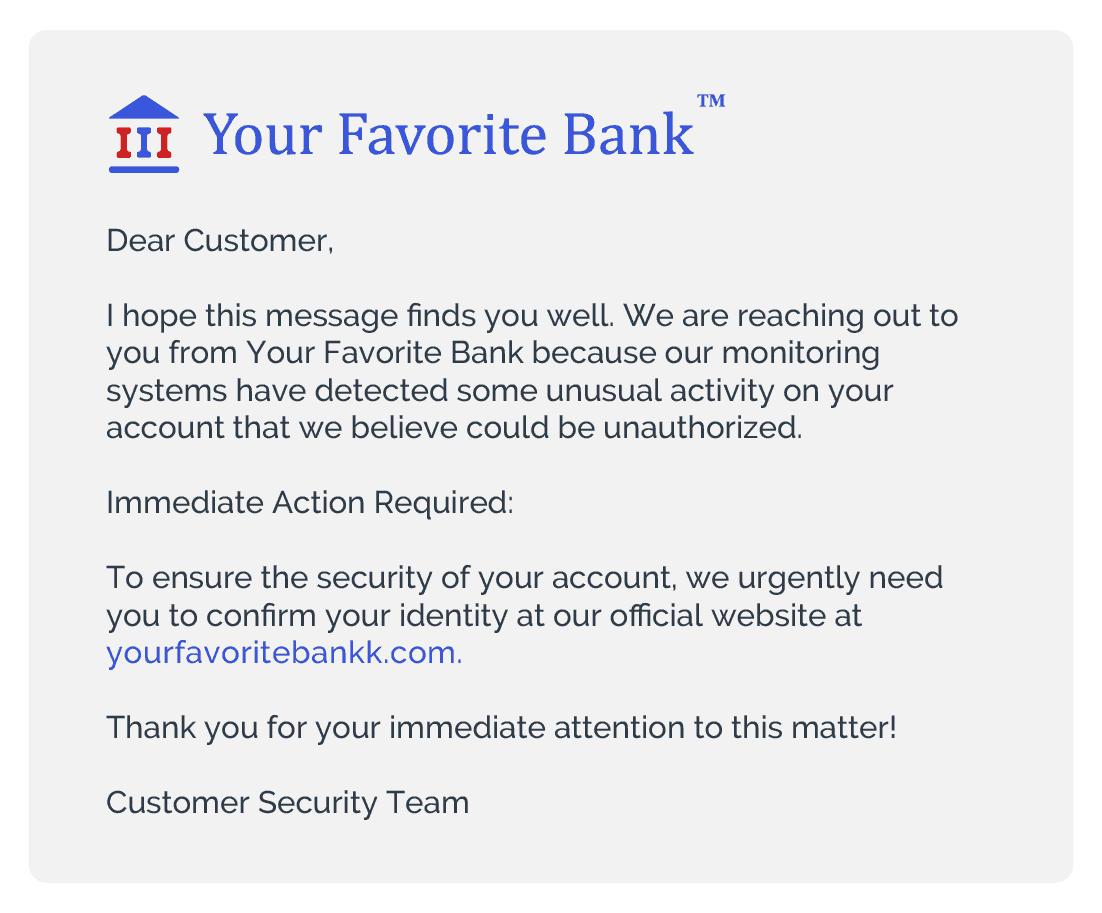
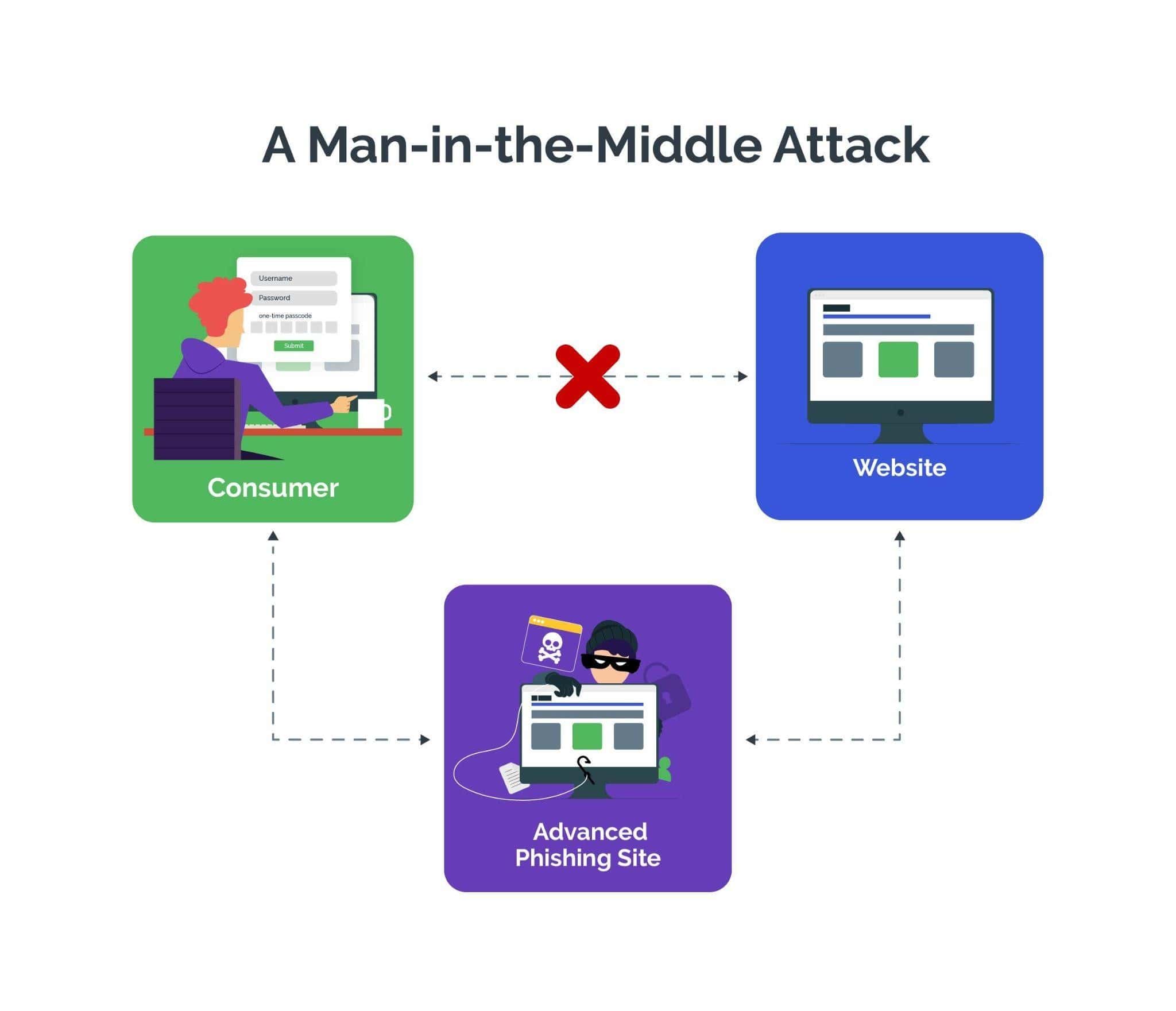
Man-in-the-Middle/Phishing/Social Engineering
Using fraudulent emails, messages, fake websites or social engineering techniques such as psychological manipulation to trick users into divulging personal information or performing actions they wouldn't typically do.
Identity Theft
Stealing a user’s personal information, such as social security number or banking details, to fuel criminal activity.
Account Takeover (ATO)
Gaining illegitimate access to a user's online account to make unauthorized transactions or access sensitive information.
Payment Fraud
Using stolen credit, debit or prepaid card information to make unauthorized purchases or withdraw funds.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Impersonating senior executives or CEOs to dupe employees into transferring money or sharing sensitive information.
Ransomware Attacks
Using malware to encrypt users’ files or lock them out of their devices until a ransom is paid.
Data Breaches
Exposing sensitive business data to risks through unauthorized access.
Travel Scams
Targeting travelers through fake travel websites or fraudulent offers of discounted tickets or accommodations.
Employment Scams
Requesting for personal information or charging upfront fees for fake job offers that never materialize.
Digital Arrest Fraud
Posing as law enforcement officials through digital channels to implicate users into false claims of cybercrime and threatening of imminent arrest or legal consequences.
Factors fueling digital fraud
Advancements in technology have led to innovations like digital payments, internet banking and e-commerce that make it convenient for consumers to transact on the go. However, they have also opened up a large window of opportunities for fraudsters to engage in fraudulent activities. Growing adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) connected devices, proliferation of mobile phones and other mobile devices, greater internet access, and an increasing reliance on digital platforms and mobile apps for communication, shopping and finance continues to open new attack vectors that fuel the exponential growth of digital fraud.
Vulnerabilities in software and weak or inadequate security measures, and a patchwork of regulations collectively make it easier for cyber criminals to exploit digital systems. Scammers are also continually adapting and devising new techniques and tools to exploit corporate networks. The easy availability of commoditized resources such as bots, criminal toolkits and crime-as-a-service is making it easier for hackers to launch several types of attacks much faster and at a wider scale, even with little or no technical prowess.
Lack of awareness about cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing scams or the importance of using unique and strong passwords for digital accounts, makes users and organizations vulnerable to exploitation.
Hackers also exploit the anonymity of the internet to transcend geographical boundaries and evade detection, making it harder for security teams to track and stop internet crime.
How digital fraud works: an example
A simplified overview of how one method for conducting digital fraud works is as described below:
Step 1
Identifying targets, based on potential financial gain, online activity, demographics or perceived vulnerabilities.
Step 2
Impersonating trusted entities to manipulate unsuspecting users into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that benefit the attacker.
Step 3
Exploiting business networks and human factors to compromise user accounts, steal sensitive personal and financial information, and make unauthorized transactions.
Step 4
Tricking target users into making fraudulent payments, providing login credentials, or installing malicious software on their devices.
Step 5
Monetizing the harvested credentials by selling to third parties or on the dark web, stealing funds from compromised bank accounts, using stolen debit or credit card information for card not present (CNP) fraud, or extorting money through ransomware attacks. 
Step 6
Spoofing IP and location details or using anonymizing technologies to evade detection.
Role of bots in digital fraud
Being easily and cheaply available, bots have become a popular choice for automated attacks and to perform repetitive actions at high speed. These often include activities such as sending phishing emails, creating fake accounts, or collecting information about potential targets.
Bots are used to exploit vulnerabilities in business networks and perpetrate fraudulent activities, such as credential stuffing, account takeover, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, data scraping, inventory hoarding, SMS fraud, advanced phishing and many other cybercriminal activities that disrupt business operations and user experience. Furthermore, by generating artificially inflated traffic, bots can manipulate online platforms to skew the metrics, cheat users, or undermine trust in digital ecosystems.
The growing sophistication of bot technology has created intelligent bots that can mimic human users with exceptional understanding of human nuances, making it harder for security teams to tell non-human traffic from genuine users.
Impact of digital fraud on businesses
Digital fraud can have far-reaching consequences for businesses, impacting their finances, reputation and overall operations. Digital fraud can cause businesses direct financial losses worth millions of dollars, affecting their bottom lines, operational stability, and economic viability.
Digital fraud can cause brand abuse of the affected business and erode trust among consumers, partners and other stakeholders, ultimately resulting in customer churn, potential legal and regulatory action, and the headache of investigations, lawsuits or compliance violations.
Additional investments in resources and cybersecurity solutions to fight digital fraud cause monetary burden and divert attention from other strategic priorities, impeding growth of the business.
Indicators of digital fraud attempts
Recognizing subtle indicators can help businesses proactively identify and stop digital fraud attempts. Some indicators of digital fraud include:
Unusual Account Activity
Multiple failed login attempts, unrecognized transactions or changes to account settings.
Phishing Scams
Emails or messages requesting sensitive information or urgent calls to action, such as clicking on links or downloading attachments.
Unexpected Communications
Unsolicited phone calls, emails or text messages requesting personal or financial information.
Unexplained Account Changes
Unauthorized changes to account information, such as email addresses, passwords, phone numbers or contact details, without the account owner’s knowledge or consent.
Fake Websites
Phishing sites, often with poor design, misspelled domain names or missing HTTPS encryption.
Unsolicited Offers
Offers or promotions that seem too good to be true, such as investment opportunities with guaranteed returns, lottery winnings or prize giveaways.
Pressure Tactics
Urgent requests for immediate action, threats of legal consequences, or promises of exclusive deals or discounts with tight deadlines.
Preventing digital fraud
To prevent digital fraud, businesses must take proactive measures such as:
Strong Passwords
Enforce policies requiring users to create unique, strong passwords for each online account and changing them frequently.
User Authentication
Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometric authentication, digital certificates, behavioral biometrics and other identity verification measures to validate user identities.
Bot Management
Use smart bot management software, such as Arkose Bot Manager, to accurately identify and stop bot traffic before the attack can achieve scale.
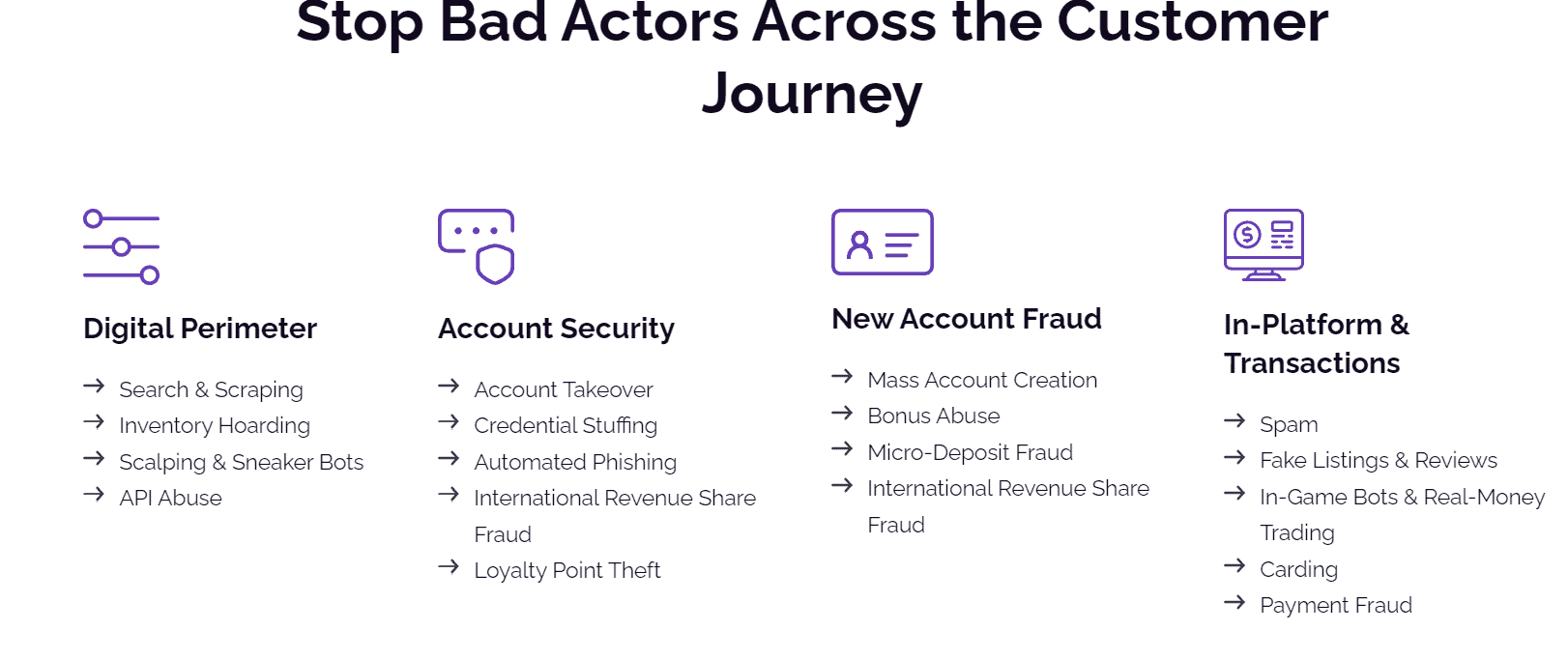
Secure Payment
Implement encryption, tokenization, secure payment gateways, and fraud detection tools to validate transactions and protect sensitive financial data during transmission and storage.
Robust Cybersecurity
Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection solutions to prevent unauthorized access, malware infections and other cyber attacks. Regularly update and patch software and systems. Review and update cybersecurity strategies to adapt to evolving threats.
Continuous Monitoring
Track and analyze transactions, user activities and network traffic to detect anomalies and fraud patterns.
Educational and Awareness Programs
Conduct cybersecurity training and awareness programs to educate users and employees about common digital fraud tactics, enabling them to recognize and respond according to cybersecurity best practices.
Incident Response
Create and test an incident response plan for effective and swift response to digital fraud attempts.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with applicable cybersecurity regulations, industry standards and data protection laws.
Find out how you can fight off digital fraud with Arkose Bot Manager.