What is a credential stuffing attack?
A credential stuffing attack refers to an automated matching of stolen usernames and passwords to find valid combinations of login credentials. Bad actors use scripts or tools that can input large volumes of stolen or leaked username and password combinations into websites, applications or services to match valid credentials with existing accounts.
Credential stuffing is the fuel that powers account takeover attacks (ATO) and often precedes them, costing businesses millions.
Reasons for the rise in credential stuffing attacks
There are multiple reasons contributing to the rise in credential stuffing attacks. First, motivation on the part of cybercriminals is strong. Potential monetary gains, through monetization of stolen account credentials or gaining access to valuable personal and financial information, incentivize attackers to engage in credential stuffing attacks.
Secondly, it’s gotten easier, thanks to widespread password reuse across multiple online platforms. The dark web and a flourishing underground economy provide cybercriminals with opportunities to buy, sell and trade compromised login credentials obtained from data breaches. Using these large databases of usernames and passwords, cybercriminals can easily access account credentials and use them to launch credential stuffing attacks.
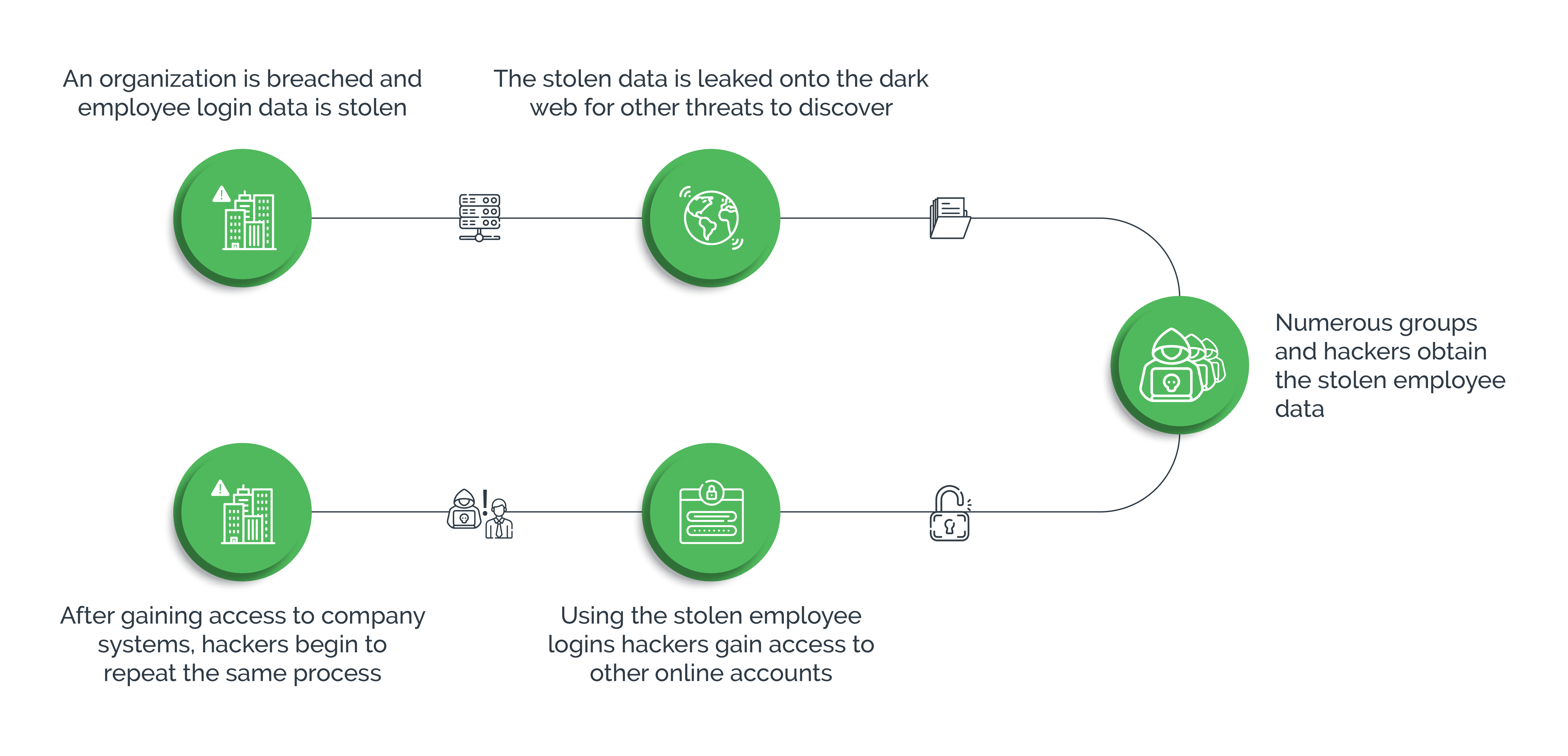
Thirdly, the increasing sophistication of automated tools and scripts enables attackers to execute these types of cyberattacks at scale with minimal effort or investment. By leveraging botnets, for example, hackers can rapidly match millions of usernames with passwords, exploit vulnerabilities in login systems, and bypass basic cybersecurity measures.
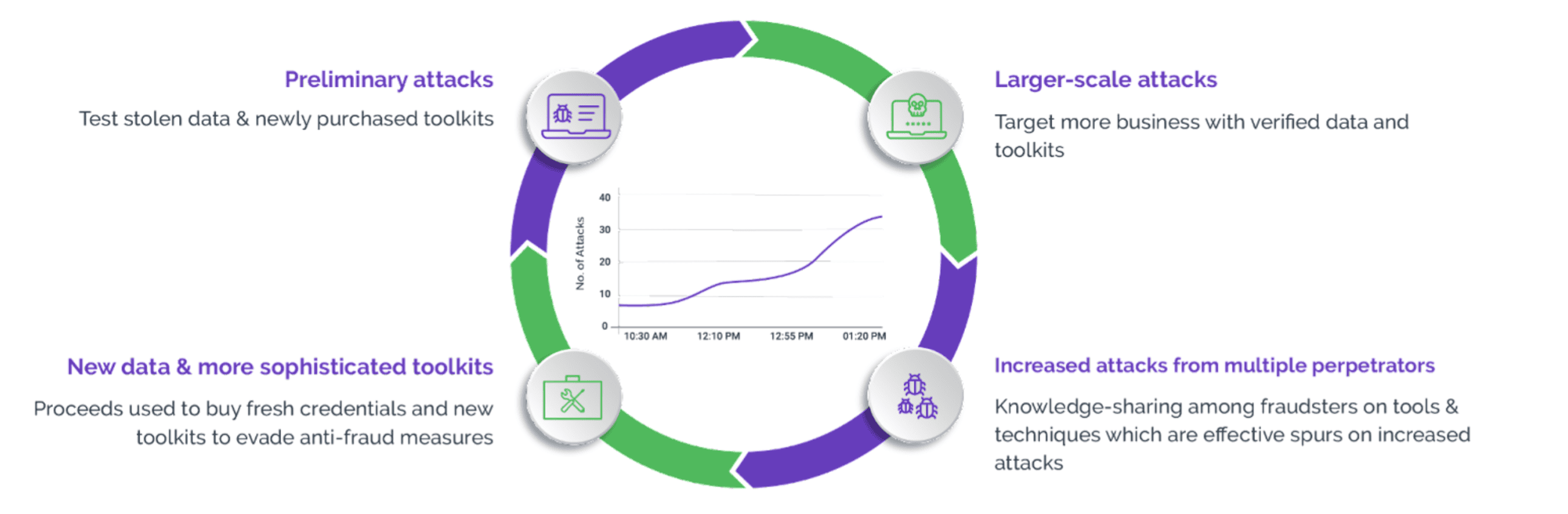
Lastly, the lack of strong authentication mechanisms exacerbates the risk of credential stuffing attacks. Inadequate bot protection measures, insufficient monitoring for suspicious login attempts and outdated password policies can create vulnerabilities for hackers to exploit and compromise customer accounts.
The role of bots in credential stuffing attacks
By enabling attackers to conduct credential stuffing attacks with minimal human intervention, bots reduce the resources and expertise required to execute this type of cyberattack. This accessibility lowers the barrier to entry for cybercriminals, making automated bot attacks a popular choice among attackers.
Because bots are readily and cheaply available, they have become the primary tool for automating the process of credential stuffing attacks. Bots can test large volumes of stolen or leaked username and password pairs across multiple online platforms much faster than a human can. This swift and automated process provides hackers with valid login credentials faster and more efficiently.
Attackers can customize malicious bots to target specific websites or services and tailor the attack strategies based on the characteristics of the targeted platform. These programmed bots can adjust their behavior to navigate through login forms, handle session management, and mimic human interactions. Furthermore, attackers use bot traffic to evade detection mechanisms such as CAPTCHA challenges or rate limiting by programming them to systematically input credentials into login forms on websites, applications or services, mimicking human-like behavior.
Credential stuffing attacks are becoming commonplace… and expensive!
Credential stuffing attacks can have a major impact on businesses as once inside an account, attackers can make fraudulent transactions, get unauthorized access to paid services, or steal sensitive financial information. These financial losses can be direct, such as fraudulent purchases made using compromised accounts, or indirect, such as expenses incurred in restoring affected accounts and systems.
Not only does this type of attack cause significant financial losses, but it can also lead to a damaged business reputation, shattered customer trust and loyalty, and lost customers. In this age of social media, disgruntled consumers may voice their discontentment on social platforms, causing negative publicity and loss of business. Rebuilding trust with customers can be a long and challenging process, requiring transparent communication, effective incident response and proactive measures to prevent future attacks.
Similarly, credential stuffing attacks can severely affect consumers. Compromise of users’ online accounts can result in identity theft, wherein personal information such as names, addresses, and financial data are stolen and used for fraudulent purposes. This can result in financial losses, damage to credit scores, and legal action. Account lockouts, resetting passwords, and restoring lost data can cause inconvenience and frustration. Furthermore, consumers may refrain from engaging with affected businesses in future out of concerns about privacy and security.
Commonly used techniques to prevent credential stuffing attacks
It goes without saying that credential stuffing attacks pose a big challenge to user account security. Businesses would do well to take preventive measures to counter this growing threat, as the return on investment (ROI) can be significant. Some common techniques that businesses can use to counter credential stuffing attacks include:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Add another layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password plus a one-time code sent to their phone, before allowing access to their accounts. MFA makes it harder for attackers to authenticate even if they have somehow obtained valid username and password pairs.
- CAPTCHA: Engage suspicious sessions in CAPTCHA challenges to filter out automated scripts and malicious bots. That said, legacy CAPTCHAs are outdated and even basic bots can easily bypass them. Therefore, businesses need smart AI-driven challenge-response authentication challenges, such as Arkose MatchKey for comprehensive protection.

- Password policies: Enforce strong password policies. Encourage users to create unique and complex passwords. Specify password requirements such as certain length and complexity levels. Regularly prompt users to update their passwords.
- Rate limiting and throttling: Implement rate limiting and throttling mechanisms to limit the number of login attempts from a single IP address or user account within a specified time frame.
- IP reputation and geolocation analysis: Monitor and analyze the reputation and geolocation of incoming login attempts from different IP addresses to identify and block suspicious traffic associated with credential stuffing attacks.
- Web application firewalls (WAF): Deploy WAF solutions to detect and block automated bot traffic, as well as for additional security features such as signature-based detection and real-time threat intelligence feeds.
- Credential monitoring and detection: Implement systems to monitor for leaked or compromised credentials on the dark web and other underground forums. This helps proactively detect potential sources of credential stuffing attacks, take preemptive action to reset passwords, and mitigate the risk of account compromise.
- User education and awareness: Educate users about the risks of credential reuse and security best practices such as the importance of using unique passwords for each online account, not sharing credentials with others, and enabling additional security features such as MFA.
Account security is critical to business growth
Attackers use advanced bots and automated scripts to scale up their attacks quickly and cost-effectively. These bots can mimic human behavior with a high degree of accuracy, while more complex tasks are outsourced to low-cost human click farms. If successful, such attacks can disrupt business operations and user experience, resulting in a significant financial loss.
Investing in robust AI-enabled bot detection and mitigation software can help protect businesses and their consumers from the onslaught of credential stuffing attacks and ensure a positive return on investment. Smart bot management solutions identify and block malicious bot traffic, trying to exploit authentication systems, using the following techniques:
- Behavioral analysis: Analyze user behavior patterns to distinguish between legitimate users and automated bots. Monitor factors such as navigation paths, mouse movements, typing speed, and interaction patterns to detect anomalies, indicative of bot activity, such as rapid, repetitive, and predictable behavior when attempting to input credentials into login forms.
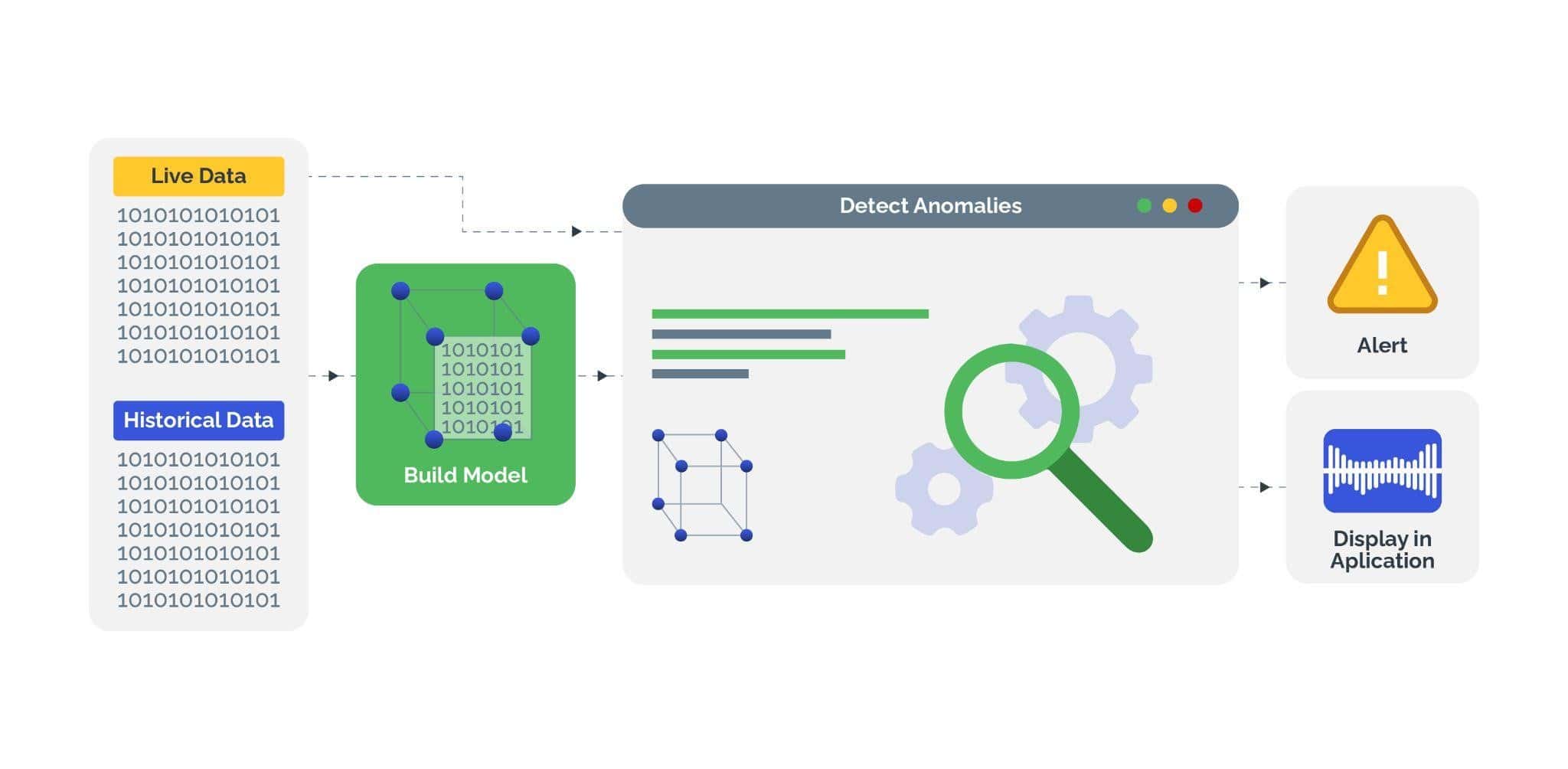
- CAPTCHA-based challenges: Differentiate between human users and automated bots. CAPTCHA challenges serve as a deterrent against automated bot attacks by introducing an additional layer of verification that is challenging for bots to bypass.
- Device fingerprinting: Identify and track unique characteristics of devices used to access online services. Analyze attributes such as device type, operating system, browser version, screen resolution, and installed plugins, to detect patterns indicative of bot activity and block suspicious devices from accessing customer accounts.
- Machine learning and AI: Adapt and improve detection capabilities based on evolving threats and attack techniques. Analyze large volumes of data and identify patterns of bot behavior to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of bot detection mechanisms over time.
Looking for more information on how to stop cyberattacks? Discover the Arkose Labs credential stuffing solution.