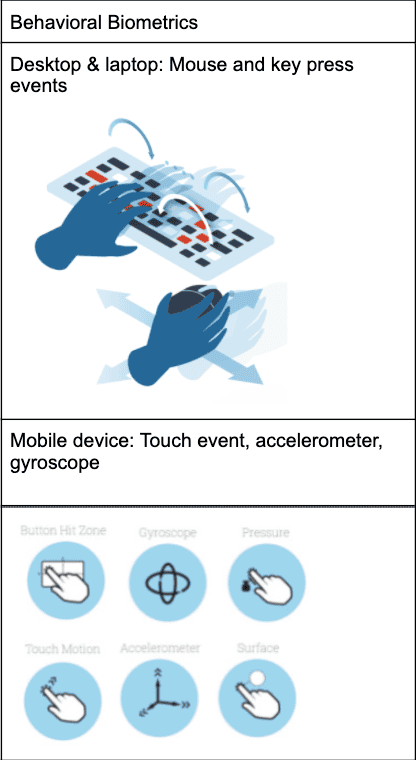
What Is Behavioral Biometrics?
Attackers are in the business of cybercrime to make money. They continuously improve their attack tactics to maximize the gains. To detect and fight such complex attacks, security vendors deploy many techniques including IP intelligence, device intelligence, rate limiting, and statistical learning. These techniques, combined with advanced web authentication methods such as behavioral biometrics, improve the ability to accurately identify attackers from genuine consumers.
Behavioral biometrics is a technology that enables security teams to analyze patterns of a consumer behavior, which helps distinguish them from bad actors. It entails analyzing user interaction with a device and includes parameters such as mouse movement, key presses, touch screen interactions, gait analysis, cognitive biometrics, and so forth. It is however, different from physical biometrics that involves human characteristics such as iris or fingerprints.
Behavioral biometrics vs behavior analysis
As explained above, behavioral biometrics is different from physical biometrics. It is also different from behavioral analysis. The latter is useful in situations where the need is to analyze what a consumer interacts with in a web service to help understand the context to the actions taken.
Types of behavioral biometrics
- Body movement: Also called kinesthetics, this category is used to analyze a consumer’s unique body movements such as posture, gait, handling a device. Every individual has a unique way of positioning the body, walking style, and holding a mobile device. For instance, position of the body can help understand the distribution of the body weight whereas gait analysis can provide insights on how swiftly the consumer moves or the length of steps taken.
- Voice inputs: It is used to analyze the patterns due to sound variations that occur when a person speaks.
- Device-based: When a consumer interacts with a device, there are imprints that can be analyzed. These imprints include keystrokes, interaction with mobile devices, cursor movement, typing speed and style.
Proper implementation is key
Formal behavioral biometrics implementation can be data-intensive and computationally expensive. However, sampling high information events instead of collecting all user interactions on a website can help reduce costs. For instance, when implemented properly, there is no need to collect personally identifiable information or username-password of a consumer during sampling.
Benefits of behavioral biometric detection
Behavioral biometrics holds immense potential in helping detect account takeover, web scraping, and fake account creation. The events collected from can help detect these attacks in a way that is independent of IP or device information. As a result, when each dataset is combined it leads to a much stronger detection signal. Supplementing other cyberattack prevention efforts with analysis of behaviors can help define custom rules on the type of behavior expected or acceptable given the user’s actions during a session, the time of day, or how other users have behaved in the past.
One of the biggest benefits is that all events are collected passively, which reduces friction during checkout, account creation, or login. This approach is beneficial for both consumers and web services, as consumers can continue with their digital activities without disruption from security measures like CAPTCHAs or rate limits, while web services benefit from better security and reduced impact on user experience.
Another key benefit of behavioral biometrics is that it makes data spoofing difficult. While it is possible to spoof information collected from client-side events, it is difficult and requires sophistication to accurately corrupt rich human interaction data versus simply spoofing something like a user agent. Attackers would need to invest time, resources, and knowledge of programming and data-savvy techniques to efficiently spoof behavioral biometric data at scale. That said, bad actors may develop new methods if there is enough incentive.
Furthermore, behavioral biometrics increases the efficiency of cyberattack efforts, as it can be used real-time as well as retrospectively to authenticate incoming traffic and detect potential attacks.
Uses of behavioral biometrics
Behavioral biometrics is an important weapon in the fight against digital abuse. It helps security teams understand the subtle usage patterns of online traffic through behavioral parameters. These insights are crucial to detect and stop bad actors early in their tracks.
Behavioral biometrics is commonly used in eCommerce, financial institutions such as banks, and access control systems.
- eCommerce: The always-on nature of eCommerce platforms requires them to offer seamless digital experience to their consumers, failing which they risk consumer churn and business going to another competing provider. Another consideration for eCommerce platforms is personalization – to highlight relevant products of interest based on consumers’ interactions.
- Financial institutions: With continuous monitoring of a consumer’s behavior, financial institutions increase their ability to verify consumers’ identity at any point during the active session, and not just at the registration or login stages. This increased visibility enhances the ability to spot malicious activity and take appropriate countermeasures in time.
- Access control: Behavioral biometrics can help analyze and flag suspicious activity for further attention, such as when an impostor tries to use stolen consumer credentials to gain access.
In addition, behavioral biometrics is being successfully used to fight remote access trojans, insider threats, USB attacks, phishing, identity theft, and so forth.
That said, mass manipulation of digital identities is making it challenging to use only pure behavioral biometrics to discern an authentic consumer from an attacker. Challenging risky users with targeted friction in the form of adaptive, step-up challenges can help stamp out cybercrime with certainty.
A behavioral biometrics example
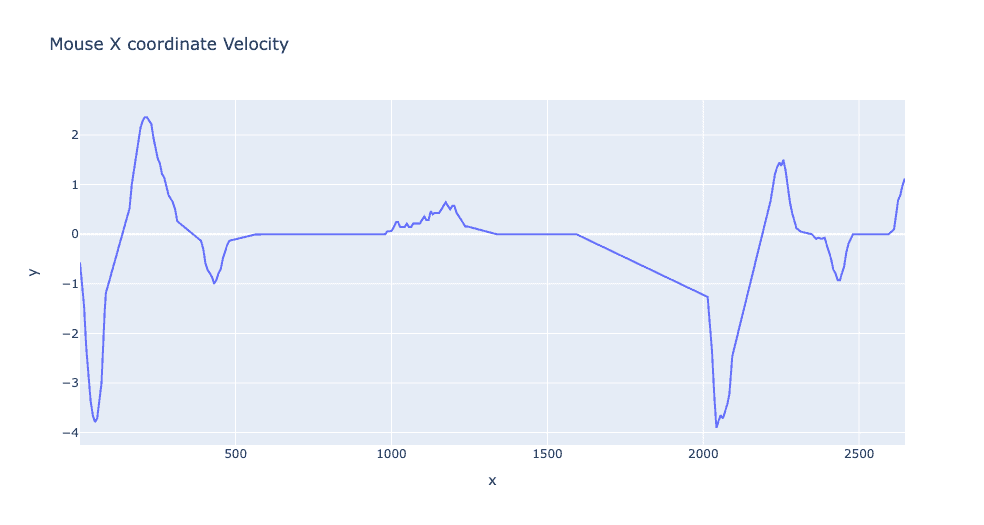
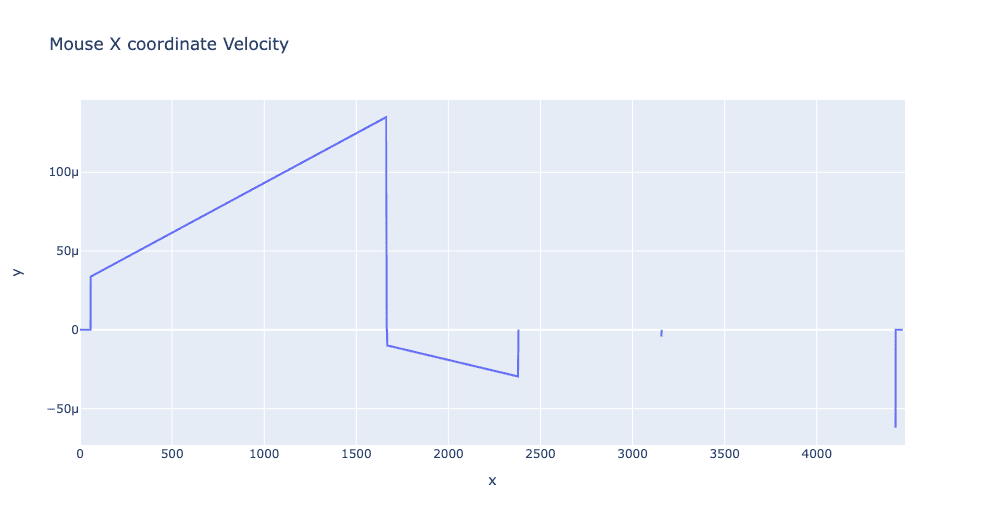
By examining the signals derived from behavioral biometrics, significant distinctions between basic automated systems and authentic human users are clear. Notably, the analysis of human-mouse velocity exposes inconsistencies and frequent spikes in mouse motion speed. Automated systems, on the other hand, tend to exhibit linear cursor velocity with minimal variability compared to human behavior.
Mouse input by a human:
Mouse input by a bot: