Credential abuse is a serious threat that affects businesses and individuals alike. Bad actors use stolen credentials in various ways to gain unauthorized access to digital accounts, bypass security measures, and carry out malicious activities. According to recent studies, credential-based attacks have caused financial losses worth millions of dollars to businesses every year.
In this type of attack, threat actors use stolen user credentials to circumvent defense mechanisms, gaining access to sensitive data, like email addresses, credit card information, and personal logins. Attackers then use these compromised accounts for nefarious purposes. In this context, understanding the nature of credential abuse and how it differs from other types of attacks is essential for protecting digital assets and preventing cybercrime.
Why is credential abuse common?
Consumer reliance on digital channels for practically every life activity is rising. This increase in the number of users and the data strewn across the internet is proving to be a hotbed for credential-based attacks. Bad actors harvest this data to fuel credential abuse and several other credential-based attacks.
Some of the prime reasons for the surge in compromised credentials are as described below:
- Data: Frequent incidents of data breach continue to provide bad actors with large volumes of users’ personally identifiable information (PII), which is used for a myriad of attacks.
- Weak Passwords: The number of digital accounts per user is multiplying, making it difficult to manage passwords for each unique digital account. As a result, users either create easy-to-remember passwords or reuse/repurpose passwords across accounts. Hackers can easily crack weak passwords and gain access to multiple accounts when a compromised password has been used for several accounts.
- Commoditized Tools: The availability of commoditized tools, toolkits, and crime-as-a-service is making it easy for attackers to abuse user credentials.
- Monetization: Attackers have several avenues available to monetize stolen credentials such as selling them to third parties or on the dark web.
- Subpar Defenses: Many businesses lack adequate protection against evolving threats, which makes them more vulnerable to credential abuse.
How credential abuse is carried out
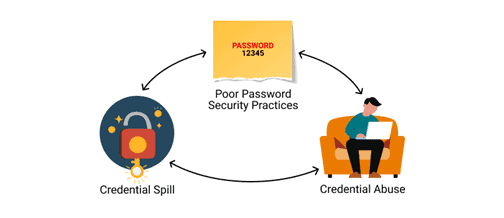
Credential abuse is a growing challenge for digital businesses globally, as stolen credentials open up a wide window of opportunities for attackers. They can use the stolen credentials in a number of ways and to target digital platforms—websites, apps, and API channels—through complex and targeted credential-based attacks.
The main steps involved in credential abuse include:
Accessing data: Large volumes of users’ personal information is freely available on the internet, which the bad actors can easily harvest. In addition, attackers can use methods such as phishing and malware to extract user data. They can also choose to buy user credentials from the dark web.
Credential testing: Attackers test the stolen user information to find valid username-password combinations. For this, they use several methods such as credential stuffing, brute forcing, password spraying, and so forth.
Credential abuse: Once valid access details are obtained, attackers can use them to:
- Monetize the username-password combinations by selling them to third parties
- Compromise accounts through account takeover attacks
- Steal money and sensitive information from the compromised financial accounts
- Use compromised accounts for financial crimes such as card-not-present (CNP) transactions and opening new lines of credit
- Commit identity fraud and identity theft
- Register new fake accounts
- Launch low-and-slow attacks
- Plant malware
How is credential abuse different from credential stuffing?
Credential abuse and credential stuffing are both forms of cyber attacks that involve the use of stolen usernames and passwords. However, they differ in their methods and goals.
Credential stuffing is an automated attack that uses stolen credentials from one website or service to gain unauthorized access to other websites or services. In a credential stuffing attack, the attacker uses a bot to rapidly test stolen credentials against multiple websites or services until they find a match, allowing them to gain access to the victim's accounts. The goal of credential stuffing is typically to gain access to sensitive information or to take over user accounts for fraudulent purposes.
On the other hand, credential abuse is a more targeted attack that involves using stolen credentials to gain access to a specific target system or network. In a credential abuse attack, the attacker typically already knows the victim's username and password, which they obtained through a separate data breach or by other means. The attacker then uses these stolen credentials to gain unauthorized access to the victim's accounts on the target system or network. The goal of credential abuse is often to steal sensitive data or to carry out other types of malicious activities on the target system.
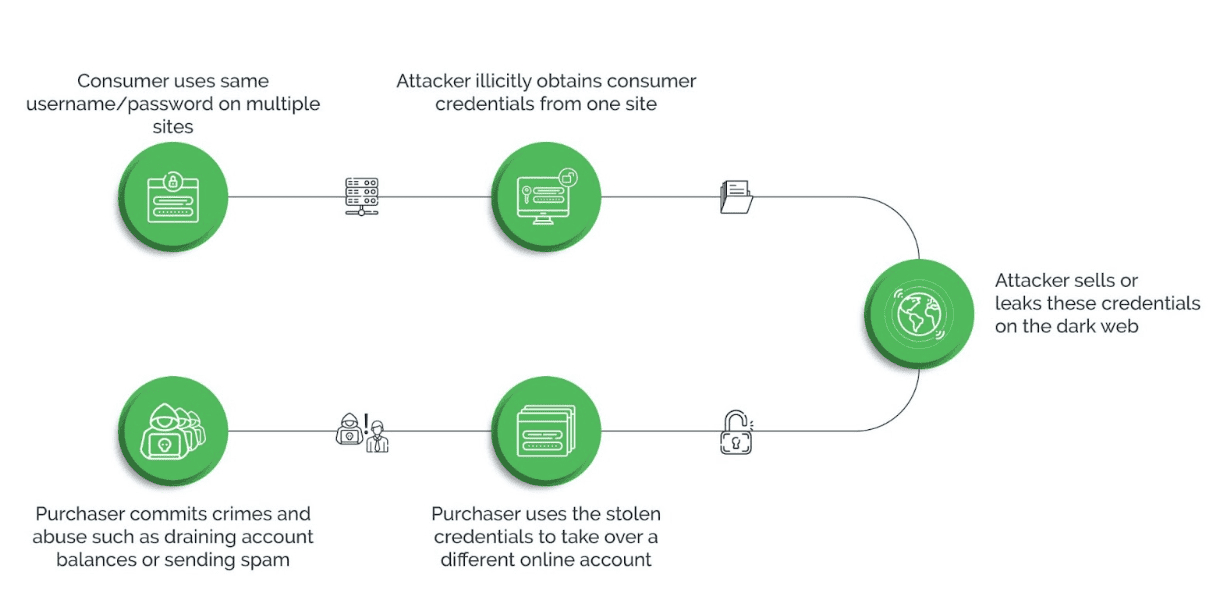
What is credential compromise?
Credential compromise is exactly what it sounds like – when a user’s login credentials have been compromised. This can happen through credential theft, credential stuffing, or some other tactic where login credentials can no longer serve their purpose of authenticating and verifying the identity of a user accessing a particular system, platform, or service because an unauthorized individual has access to those credentials.
How does credential abuse impact businesses?
Credential abuse can have far-reaching effects on the overall security and bottom-line of an organization. It can power a plethora of criminal activities, causing financial and reputational damage to the affected business. These attacks can affect the operational efficiency of the affected business, resulting in discontent customers and loss of revenue.
Credential abuse is equally dangerous for consumers as they are exposed to heightened risk of identity theft, which can obliterate their digital lives. Credential compromise can take a toll on the mental well-being of the affected customers as they may be denied loans or credits, barred from making digital transactions. Further, identity theft can result in customers spending time and effort to get their digital identities restored, which may not even happen for sure.
Identifying credential abuse attempt
Attackers try to monetize newly minted lists of valid username-password combinations through credential abuse as soon as they can. This is because once a data breach is detected, passwords may be reset quickly, reducing the success rate of credential abuse.
To identify credential abuse, businesses can look for the following telltales:
- Anomalous activity: A surge in unusual activity such as unexplained increase in chargebacks or anomalous activity in financial accounts
- Login attempts: Unexpected login attempts from unknown locations or devices
- Password resets: A sudden jump in password reset requests indicates possible credential abuse
- Customer support: A surge in customer support requests is a telltale of possible attempts of credential abuse
Tips to prevent credential abuse
To prevent the aftermath of credential abuse, it is critical that digital businesses are able to spot anomalous activity and devious patterns. The sooner they are able to identify credential abuse attempts, the better they can protect themselves and minimize the damages.
There are certain measures that businesses can take to prevent credential abuse. Some of the commonly used methods are described below:
- Use 2FA: Adding an extra layer to authenticate users can help enhance security.
- Strong Passwords: Often, even organizations use default or weak passwords that increase their risk of credential abuse. Using strong passwords and changing them frequently can improve security.
- Continuous Monitoring: Keeping a constant vigil on the incoming traffic can help spot suspicious activity early, enabling taking timely countermeasures.
- Plug-in Loopholes: Attackers exploit loopholes in business networks to gain unauthorized access. Keep software updated and implement the latest patches.
- Review Strategy: Frequently review the security strategy to identify areas of improvement and implement the required changes.
- Use Anti-abuse Solutions: Fortifying defenses with solutions that can efficiently detect attempts of credential abuse.
- Partner with a Good Vendor: Choose a reliable vendor, like Arkose Labs, that can proactively fight credential abuse attempts and shares actionable intelligence to fight evolving threats for long-term protection.
Prevent credential abuse with Arkose Labs
Arkose Labs empowers businesses to proactively prevent credential abuse while keeping user experience at the forefront. Using a unique combination of real-time risk assessment, machine learning, data analytics, risk insights and unmatched attack response, Arkose Labs provides digital businesses with a robust solution that detects credential abuse early in its tracks, affording businesses to counter them immediately.
Arkose Labs establishes a behavioral baseline for all users and assets in the network and assigns risk scores for users that deviate from this baseline. Combining this risk score with scores of digital intelligence Arkose Labs empowers digital businesses to mitigate the threats of credential abuse