What are OTP Bots?
The bots that enable attackers to extract one-time passwords from consumers without human-intervention are commonly known as OTP bots. Attackers use these programmed bots to call up unsuspecting consumers and trick them into divulging their two-factor authentication codes. They then use these codes to authenticate and complete unauthorized transactions from compromised accounts.
The Use of OTP Bots is on the Rise
The use of OTP bots is on the rise as they are easy to use and cost-efficient relative to the potential monetization from a successful attack. Many businesses are using multi-factor authentication (MFA) on their websites and apps to authenticate users. In addition to providing a username and password, most digital transactions require consumers to authenticate themselves using a one-time password (OTP) code they receive through an SMS message. Also, there are apps that generate tokens for consumer authentication.
This two-factor authentication is providing attackers with ample opportunities to intercept, mis-direct, or spoof the SMS codes and app-generated tokens. Attackers use OTP bots to steal these codes and tokens from crypto exchanges, email services, and banks.
OTP Bots are Easy to Access
The success of OTP bots in enabling attackers to access authentication codes and tokens has led to a proliferation in bot-based services. OTP bot services cost anywhere from $40-$100 per week of unlimited use to $4,000 unlimited-use subscription for lifetime. BloodOTPbot, Otp.agency, SMSRanger, and SMS Buster are some of the many OTP bot services available readily to the attackers.
OTP bots are easily available in several underground communities. Telegram chat rooms are replete with chatter on sale and purchase of ‘OTP bot services’ and how they help attackers profit from exploiting consumers’ accounts on social media, financial, fintech, and crypto platforms. As mentioned earlier, there are many bot-based services that attackers can access at a subscription fee.
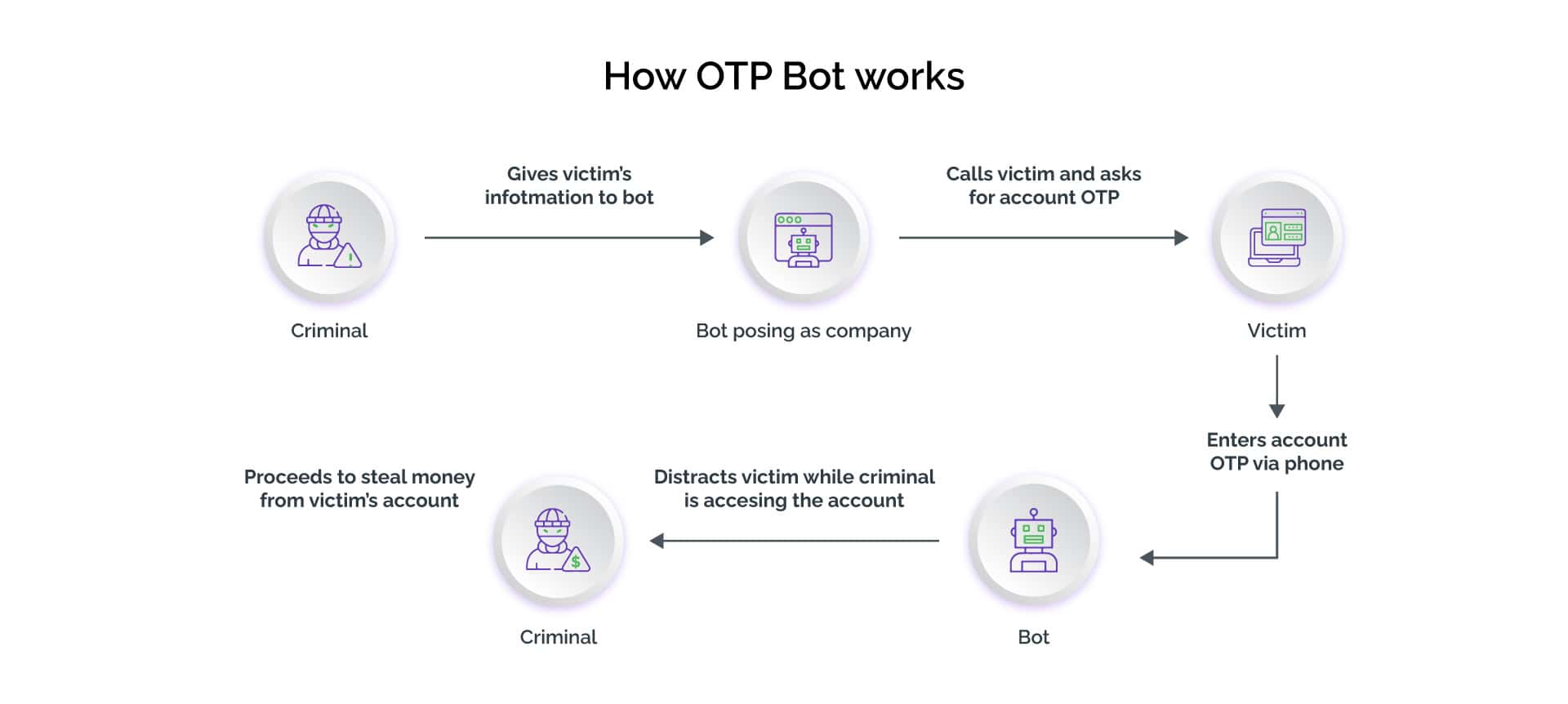
Here's How OTP Bots Work
OTP bots use social engineering to trick a consumer into sharing sensitive information about digital accounts. Attackers use them for international calling with multiple call scripts in several types of voice accents.
While attempting to log into a potential victim’s digital banking account, the attacker feeds the OTP bot with the consumer’s phone number and the name of the bank. These inputs prompt the OTP bot to initiate a call to the victim and dupe them into divulging the 2FA code (OTP or token), account PIN, and other personally identifiable information. For instance, an OTP bot would call consumers about a suspected unauthorized activity on their bank accounts, urging them to promptly enter the OTPs generated on their mobile phone’s app for their account security. These bots create panic and a sense of urgency among consumers to act. Moreover, they take advantage of consumers being habitual of using codes to authenticate while speaking to customer service executives. As soon as the consumers enter the codes, attackers can see them in real-time on the service provider’s website. They can then use these codes to complete the unauthorized transactions.
OTP Bots Help Scale up the Attack
Using social engineering to dupe consumers into divulging OTPs and other sensitive information is a manually intensive activity. OTP bots automate the process and contact victims automatically once appropriate details are entered.
Automation allows attackers to scale up the attacks to intercept and phish OTPs in large volumes. The larger the number of victims, the greater the returns. As a result, using OTP bots, attackers are able to maximize the returns from relatively lower investments. Digital businesses, however, are suffering substantial losses due to OTP bots.
Bots can Bypass OTPs
In addition to intercepting OTPs, attackers can use bots to bypass OTP-based two factor authentication verification altogether. Since an OTP is a numeric or alphanumeric string of characters, it is possible to manipulate the OTP schema. Some of the tactics attackers use to bypass OTPs on websites and apps include response manipulation, brute forcing, SMS forwarding, and broken authentication.
Businesses Must Act Urgently
Designed as a simple 2FA solution to protect consumer and business interests, SMS-based OTPs and app-generated tokens are proving to be a weak link in security. Attackers are increasingly using specialized OTP bots to intercept codes. Digital businesses must take urgent steps for bot detection and to prevent OTP bots from causing damage to business and consumer interests.
Businesses must realize that attackers use OTP bots after they have successfully compromised consumer information including bank account details and phone numbers. Usually, attackers use malware infection and resort to credential stuffing attacks, password spraying, and brute forcing for account takeover of consumer accounts. Therefore, businesses must make greater efforts towards ensuring account security of their consumers’ accounts.
In addition to educating their consumers against answering unsolicited calls or messages urging them to confirm a 2FA code, digital businesses can leverage threat intelligence for fraud prevention and to help detect and remediate the compromised accounts.