The emergence of the gig economy, a model where individuals exchange assets and services, has profoundly disrupted conventional business and trade norms. This innovative commerce design, also known as the sharing economy, has empowered individuals to lease accommodations, hire transportation vehicles, extend loans, and engage in an array of services directly with their peers.
However, as the prominence of sharing and gig economy platforms has surged, so too has the incidence of cyberattacks. Threat actors assume false consumer identities, breach legitimate accounts, and establish bogus provider profiles, all aimed at defrauding authentic users. In this world, the bedrock of trust stands as a key factor in sustaining the gig economy's momentum. As such, protecting these platforms against attackers has become an imperative of the highest order.
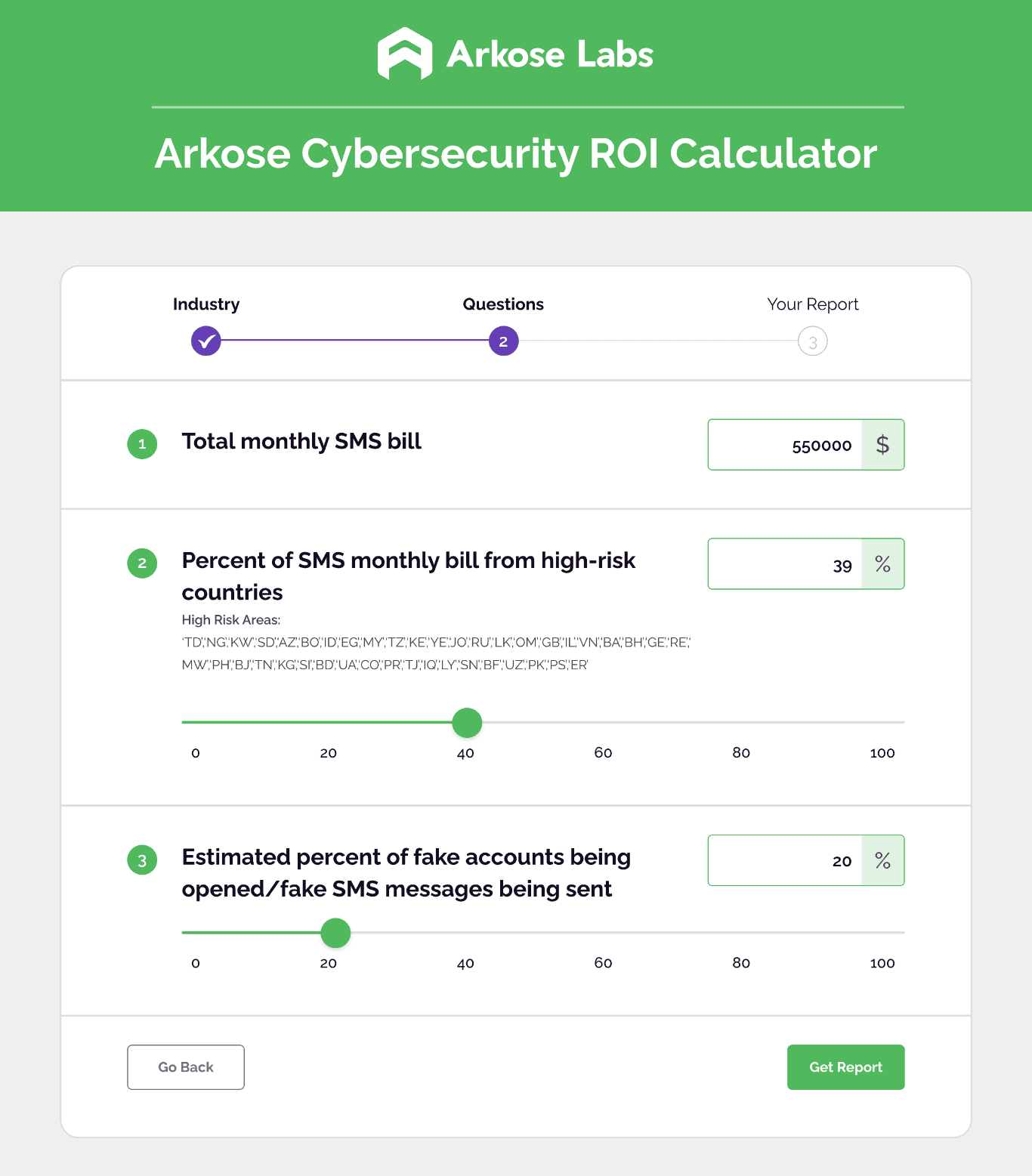
How much is your business losing to SMS toll fraud?
Find out today with our IRSF Calculator!
Bot attacks on gig economy rising
Gig economy companies like TaskRabbit, Uber, and Upwork are vulnerable to bot attacks due to several factors inherent to their business models and operations. These vulnerabilities stem from the nature of gig platforms and the characteristics of the gig economy itself:
- Large Scale and Complexity: Gig economy platforms often manage a massive number of users, transactions, and interactions. This complexity can make it difficult to distinguish between legitimate users and malicious bots, providing a cover for automated attacks.
- High Transaction Volume: Gig platforms frequently handle a significant volume of transactions, which can attract bots looking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or data theft.
- Automation Dependency: Gig economy platforms rely on automation to facilitate quick and efficient matching of service providers with consumers. However, this same reliance on automation can also attract malicious bots attempting to manipulate the system for their benefit.
- Limited Screening of Service Providers: Gig platforms may not thoroughly screen all service providers due to the sheer volume and speed at which they onboard new users. This lack of comprehensive vetting can allow bots or malicious actors to infiltrate the system.
- Monetary Incentives: Bots often target gig platforms to exploit monetary incentives, such as referral bonuses or promotions. They can automate actions that trigger these incentives, leading to financial losses for the platform.
- Fraudulent Activities: Bots can engage in various fraudulent activities within gig platforms, such as fake job postings, fake reviews, or fake user interactions. These activities can undermine trust in the platform and its users.
- Personal Data Harvesting: Bots may attempt to harvest personal data from users, drivers, or businesses registered on the platform. This data can be used for identity theft, phishing attacks, or other malicious purposes.
- Variety of Attack Vectors: Gig platforms offer multiple entry points for bots, including user registration, job posting, messaging, payment processing, and more. Each of these entry points presents an opportunity for different types of bot attacks.
To combat these vulnerabilities, gig economy companies need robust bot management solutions that combine machine learning, behavioral analysis, and real-time monitoring to identify and mitigate bot attacks effectively while ensuring a seamless experience for legitimate users and service providers.
Threats to the gig economy
Companies in the sharing economy also need to keep the following attack in mind, including how real scenarios can play out unexpectedly:
1. SCENARIO: SMS Toll Fraud
Yes, gig economy businesses can be vulnerable to SMS toll fraud. Also known as IRSF, SMS fraud or SMS pumping, this attack involves sending a high volume of text messages to premium-rate numbers or engaging in other fraudulent activities through SMS communications. While the primary goal of gig economy platforms is to facilitate connections between users and service providers, malicious actors can exploit the platform's messaging features to conduct SMS toll fraud.
For example, in the gig economy context, attackers might send fraudulent job offers or payment requests to freelancers or service providers via SMS, directing them to respond or take actions that result in monetary losses. Alternatively, attackers might impersonate the platform itself and request sensitive information or payments through text messages.
Gig economy businesses that heavily rely on SMS communications as part of their operations can potentially suffer financial losses, reputation damage, and user trust erosion if SMS toll fraud is not adequately addressed. Implementing preventive measures, such as using bot management solutions like Arkose Labs’ Bot Manager, can be crucial in mitigating these risks and ensuring a secure environment for both users and service providers.
2. SCENARIO: Fake Profile Assault
A young entrepreneur named Maria launched her new business, “UrbanTasker,” an app used to connect local freelancers with those in need of various services. It was a hit among users, but little did Maria know that a nefarious group of attackers had set their sights on exploiting her platform.
Creating fake profiles and listings, the criminals advertised enticing services at unbeatable prices on Maria’s site. Unsuspecting customers booked these services, granting the criminals access to sensitive data through malware-laden devices. Simultaneously, the attackers inundated UrbanTasker with fake service requests, launching a DDoS attack that crippled the platform. Exploiting the chaos, criminals extracted valuable data from compromised servers.
What should Maria do?
Find a strategic approach that combines real-time threat detection, dynamic risk assessment, and the best CAPTCHA in the business, Arkose MatchKey, to effectively identify and block bad traffic while ensuring a seamless experience for legitimate users.
3. SCENARIO: P2P Attacks
In the realm of personalized travel experiences, TravelBud, founded by entrepreneur Alex, revolutionized the way travelers connect with locals for authentic adventures. But as the platform gained popularity, a group of attackers noticed a ready website vulnerability to exploit.
Exploiting TravelBud's peer-to-peer structure (P2P), the attackers took advantage of its decentralized nature to craft bogus profiles. These fake account profiles advertised alluring excursions at unbelievable prices, tempting unsuspecting travelers. Little did these travelers know, by engaging with these fraudulent offers, they unknowingly downloaded malware onto their devices.
As a result, the attackers initiated a P2P attack of their own. Leveraging the network of TravelBud users, they flooded the platform's servers with a relentless barrage of fake adventure requests. This strategic move created chaos and confusion, paralyzing the platform's normal operations and damaging customer trust.
What should Alex do?
He needs Arkose Bot Manager to detect and prevent bad bots from creating fake accounts and wreaking havoc on his site. The adaptive step-up challenges and real-time risk assessment of Arkose MatchKey would ensure only legitimate users engage with the challenges, mitigating the risk of P2P attacks, fake profiles, and malware downloads.
4. SCENARIO: Account Takeover
LunchBucket, a popular foodie platform, drew attackers’ attention due to its thriving gig economy ecosystem. Hackers identified a weakness in the platform's security and initiated an account takeover (ATO) attack. Leveraging stolen email and password combinations from previous breaches, they gained access to user accounts with reused credentials.
Once inside, the scammers changed account details and offered attractive services at unusually low rates. These offers contained hidden malware, infecting users' devices upon engagement. This provided the attackers control over compromised systems, risking personal and financial data exposure.
Simultaneously, the attackers manipulated the platform's messaging, spreading their fake offers further. As the attack spread, Luckbucket's credibility suffered, and user trust eroded. Despite the platform's efforts to counteract the situation, considerable damage was done.
What should LunchBucket do?
This incident underscored the necessity of strong web authentication methods, regular security checks, and user education on password security. LunchBucket had to bolster its security, implement multi-factor authentication, and conduct a user awareness campaign to prevent future takeovers and regain user confidence.
5. SCENARIO: API Abuse
BreakNeck, a bustling gig economy platform for bikers, fell victim to an attack exploiting its APIs—which are like bridges that allow different software applications to communicate and exchange data. In this case, hackers identified vulnerabilities in BreakNeck’s APIs, which serve as the connection between its services and external apps.
The attackers used these vulnerabilities to launch automated bot attacks, flooding BreakNeck’s APIs with an excessive number of requests. This deluge overwhelmed the systems and caused disruptions, making it difficult for legitimate users to easily access the platform. Attackers simultaneously manipulated API endpoints to extract sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and transaction details. With this data, they could potentially engage in identity theft, financial fraud, or sell the information on the black market.
Word spread and BreakNeck’s tough reputation took a hit, as users stopped trusting the platform. The business responded by implementing measures like rate limiting on APIs to prevent excessive requests and enhancing overall security protocols.
What should BreakNeck do?
This business needs to recognize the critical importance of securing APIs, maintaining vigilance against automated attacks, and promptly addressing security issues to protect the integrity of its gig economy platform.
6. SCENARIO: Spam & Phishing
In a targeted attack on GigEats, a prominent gig economy platform linking local restaurants with freelance delivery drivers, a skilled cybercriminal employs a multi-phase strategy of attack. Beginning with meticulous research, the actor identifies weaknesses within GigEats' security framework, acquiring insights into users, drivers, and partners. As a result, a false email address and website are artfully crafted, mirroring the platform's official communication and appearance.
The attacker then initiates their assault by sending personalized spear-phishing emails to a select group of GigEats drivers, masquerading as the platform's support team. The deceitful email alleges a security breach, coercing drivers into urgently updating their account information via a provided link—a link that leads to a counterfeit login page purposefully designed to harvest login credentials.
With pilfered access, the attacker infiltrates multiple driver accounts, manipulating settings and payment details to redirect earnings toward their controlled bank account. Expanding the breach's scope, the assailant switches tactics, amassing phone numbers of GigEats users and dispatching spam SMS messages.
What should GigEats do?
Arkose Labs can safeguard GigEats from fraudulent account creations, ensuring that only genuine users and drivers are granted access. Through real-time risk assessments and adaptive authentication techniques, Arkose Bot Manager effectively differentiates between legitimate users and malicious entities aiming to exploit the platform for spam or phishing endeavors. Our cutting-edge technology excels in identifying and halting deceitful transactions, promptly detecting any attempts to manipulate payment details or divert earnings illicitly. Our advanced bot detection further fortifies GigEats' defenses, preserving the integrity of the platform and maintaining the trust of users and drivers alike.
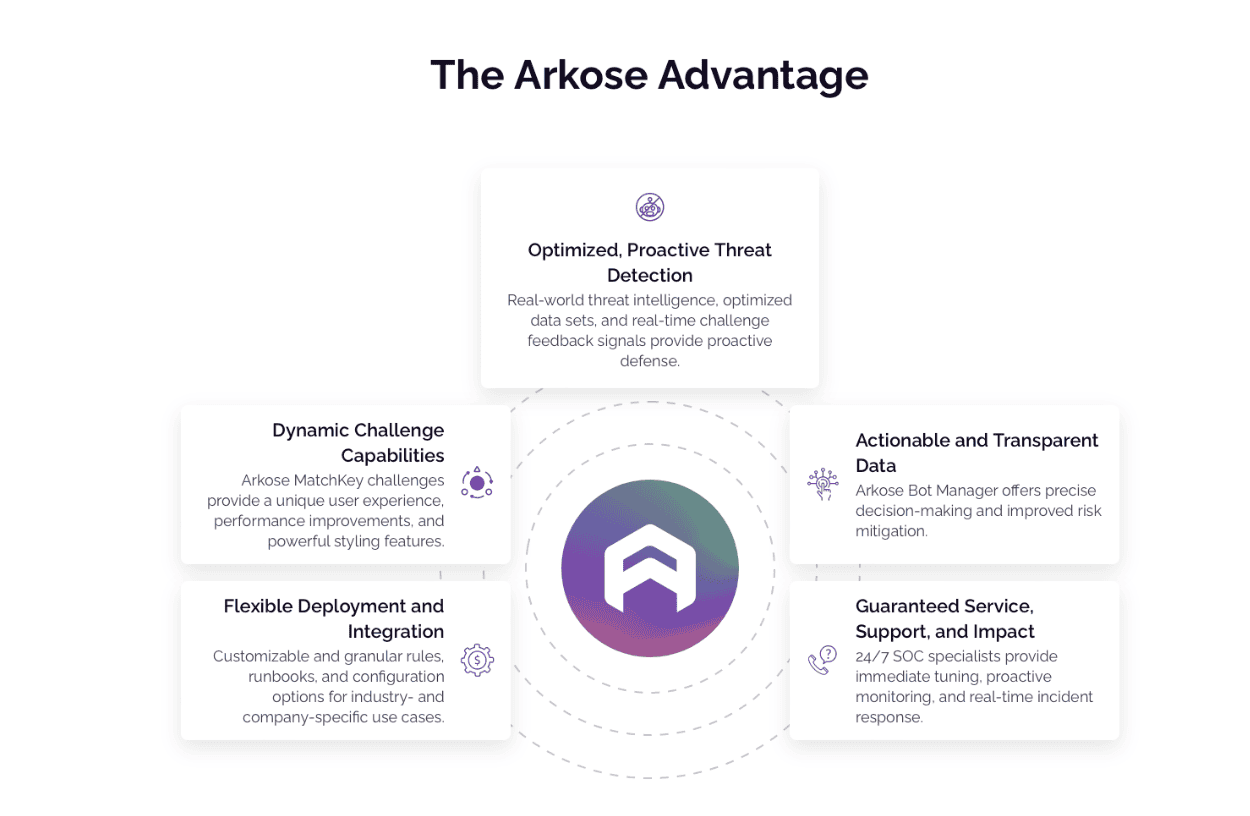
Arkose Labs protects the gig economy
It’s critical for sharing economy platforms to root out malicious activity without placing too much burden on good users. The usability and seamless experience of these services makes them appealing, an experience that should not be lost in the process of fighting cybercrime.
Arkose Bot Manager technology is tough on bots and human criminals—but easy on legitimate users. We take a zero-trust approach to all traffic. Since data has been corrupted at scale, digital identities cannot be reliably trusted. Our platform protects all user interactions on P2P websites and apps using a combination of risk profiling and enforcement challenges.
Using a variety of digital “telltales” analyzed in real-time, Arkose Labs can accurately distinguish between bot traffic, human attackers, and good users. This data is supplemented with intelligence from across our vast network, meaning criminal activity already spotted elsewhere will be automatically flagged before it attacks your website. Suspicious traffic is faced with a step-up authentication challenge from Arkose MatchKey that is near-impossible for bots to solve, thereby sapping the time and resources of digital attackers. Good users will rarely see it, and if they do, the challenge can be solved in less than three seconds.
Arkose Labs prides itself on a high level of client service. The engagement does not end after implementation. Rather, it is an ongoing partnership, with a dedicated managed services team ready to help clients analyze and problem-solve any concerns that may arise and provide answers quickly. Call us today and talk to an expert!