According to a recent 2023 security report, phishing attacks are now the most common form of cybercrime, with an estimated 3.4 billion spam emails sent each day.1 Although Google typically blocks around 100 million phishing emails daily, 92% of businesses report they’ve still received at least one compromised email.2 As a result, bad actors continue to evolve and update their phishing attack techniques, hoping they can push these startling numbers even higher.
What is a phishing attack?
Phishing is the practice of attackers sending malicious emails meant to lead users to fall for a scam. Phishing attacks attempt to trick users into clicking on web links that will download malware or redirect to a malicious website with the intent of gathering private information such as login credentials, multi-factor authentication (MFA) tokens, and financial information.
Phishing emails and phony websites frequently appear to be from well-known people or organizations, such as the victim's bank, place of employment, or institution. Attackers try to gather sensitive data from these websites, such as payment information or usernames and passwords.
What is a phishing kit?
A phishing kit is a collection of malicious tools, resources, and templates designed to facilitate and automate the creation and deployment of phishing attacks. These kits are typically used by cybercriminals to impersonate legitimate organizations, trick users into revealing sensitive information, and conduct various forms of online fraud, including stealing login credentials, financial data, or personal information.
Phishing attack methods have evolved to using pre-packed phishing kits. Phishing kits contain all the infrastructure needed for a phishing campaign, including:
- scripts
- templates for creating fake emails and websites
- a web server
- storage used to collect credentials
The attackers also register dozens of domains to avoid being detected by WAF-deny lists and spam filters.
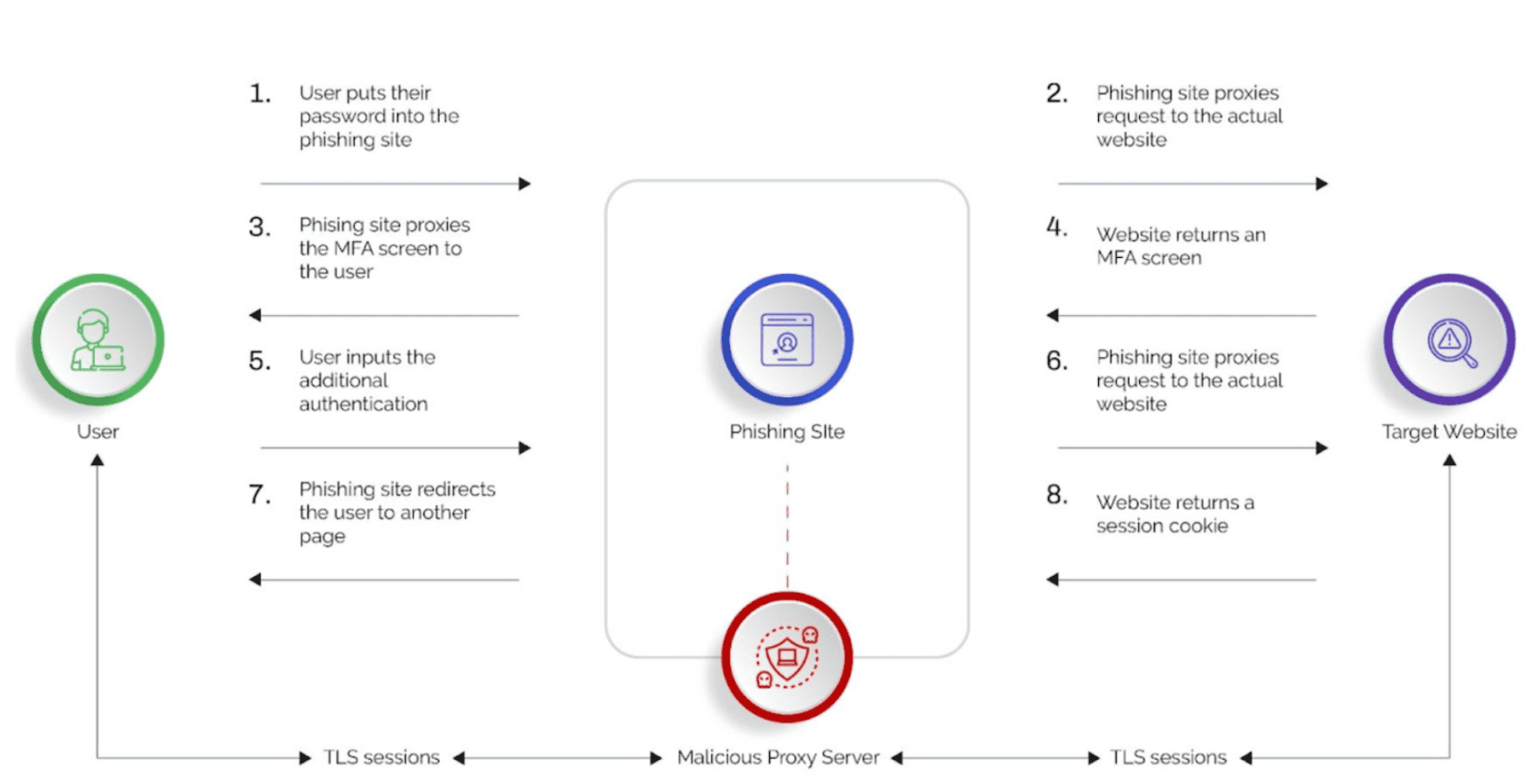
The latest evolution of phishing kits is the Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) toolkit where toolkits act as malicious reverse proxy servers of online services, mirroring target website contents to users while extracting credentials like MFA tokens and session cookies in transit. The MITM phishing kits also automate the harvesting of two-factor authenticated (2FA) sessions.
Some of the most widely used MITM phishing toolkits are Evilginx and Modlishka. EvilProxyis the most recent and uses the same “reverse-proxy” approach to lure victims to phishing sites and then sniff out the traffic to extract credentials and MFA tokens.
Phishing-as-a-Service
Caffeine is another phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform that streamlines the process of carrying out phishing attacks. Caffeine's advanced phishing features include:
- tools for customizing dynamic URL schemas to aid in dynamically generating pages with victim-specific information
- first-stage campaign redirect pages
- final lure pages
- IP blocking options for geo-blocking.
Attackers register for an account that provides immediate access to the "store," where they can find phishing campaign creation tools and an overview dashboard, and also purchase a subscription license.
Anatomy of a phishing attack
However, this approach breaks down when the site employs security measures that cannot be proxied, require user interaction, and are difficult to automate. The adaptive challenge response offered by Arkose Labs as part of the Arkose Bot Manager solution is one such solution that cannot be automated by the MITM reverse proxies.
Phishing protection from Arkose Bot Manager
Arkose Bot Manager combines highly-transparent detection with targeted attack response to catch cyberattacks early in the customer journey, without impacting good users. The solution is configured on the website's login and registration workflows prior to the MFA step. The login or the registration workflows can be completed provided the web server receives the token issued by the Arkose platform on successful completion of the detection and adaptive challenge response process.
Arkose Bot Manager’s new phishing detection not only protects from man-in-the-middle attacks by requiring our token to be present, but also in some cases alert the end consumer about the phishing attack.
Phishing Attack without Arkose Phishing Protection
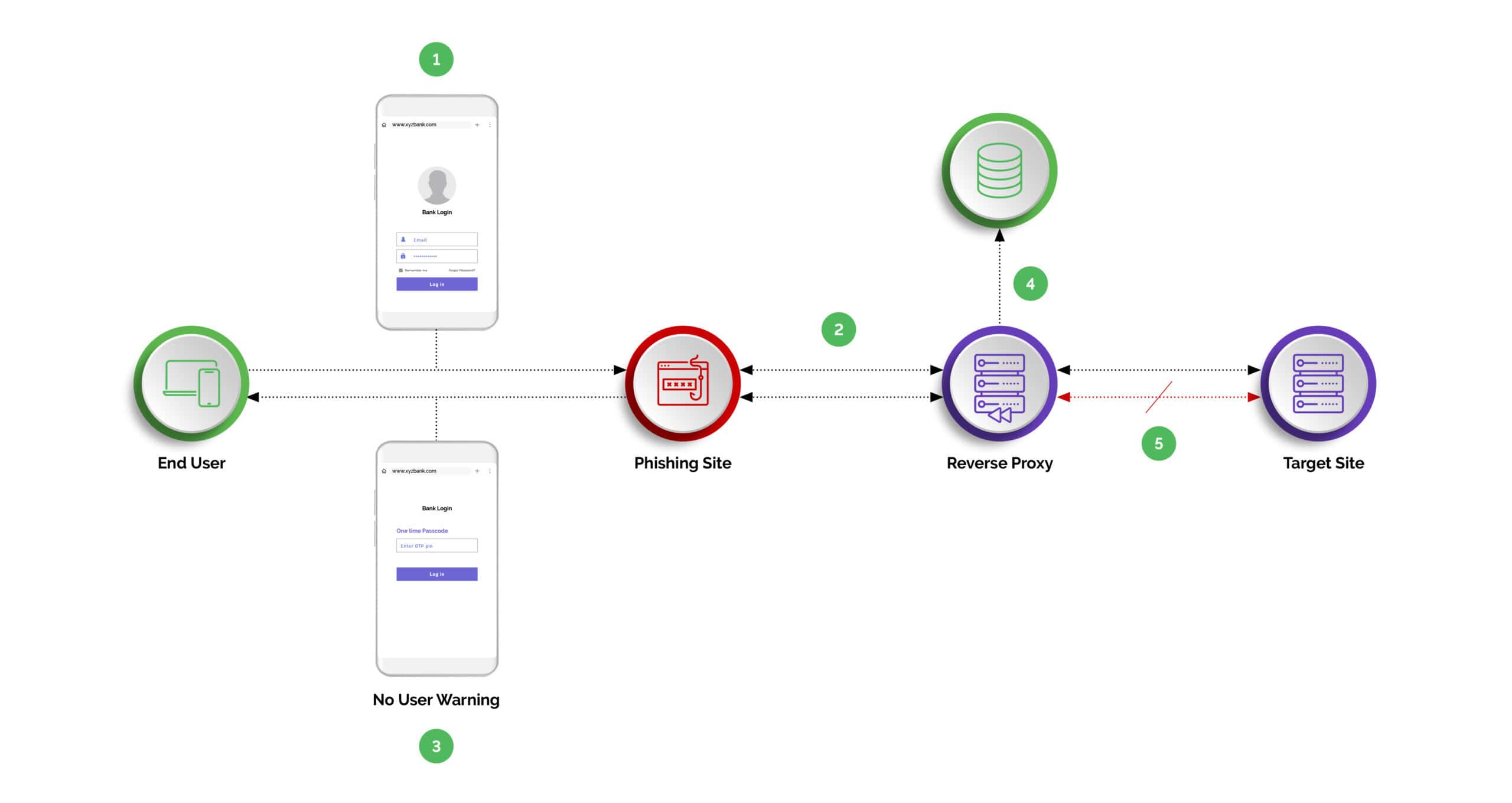
- Step One: User clicks on the malicious url/link.
- Step Two: Phishing site returned to the user while reverse proxy sniffs the traffic to the target site.
- Step Three: The user enters the credential including the 2FA/MFA Tokens.
- Step Four: The reverse proxy sniffs and harvests the token for malicious use.
- Step Five: Reverse proxy completes the transaction on the target site.
Phishing Attack With Arkose Phishing Protection
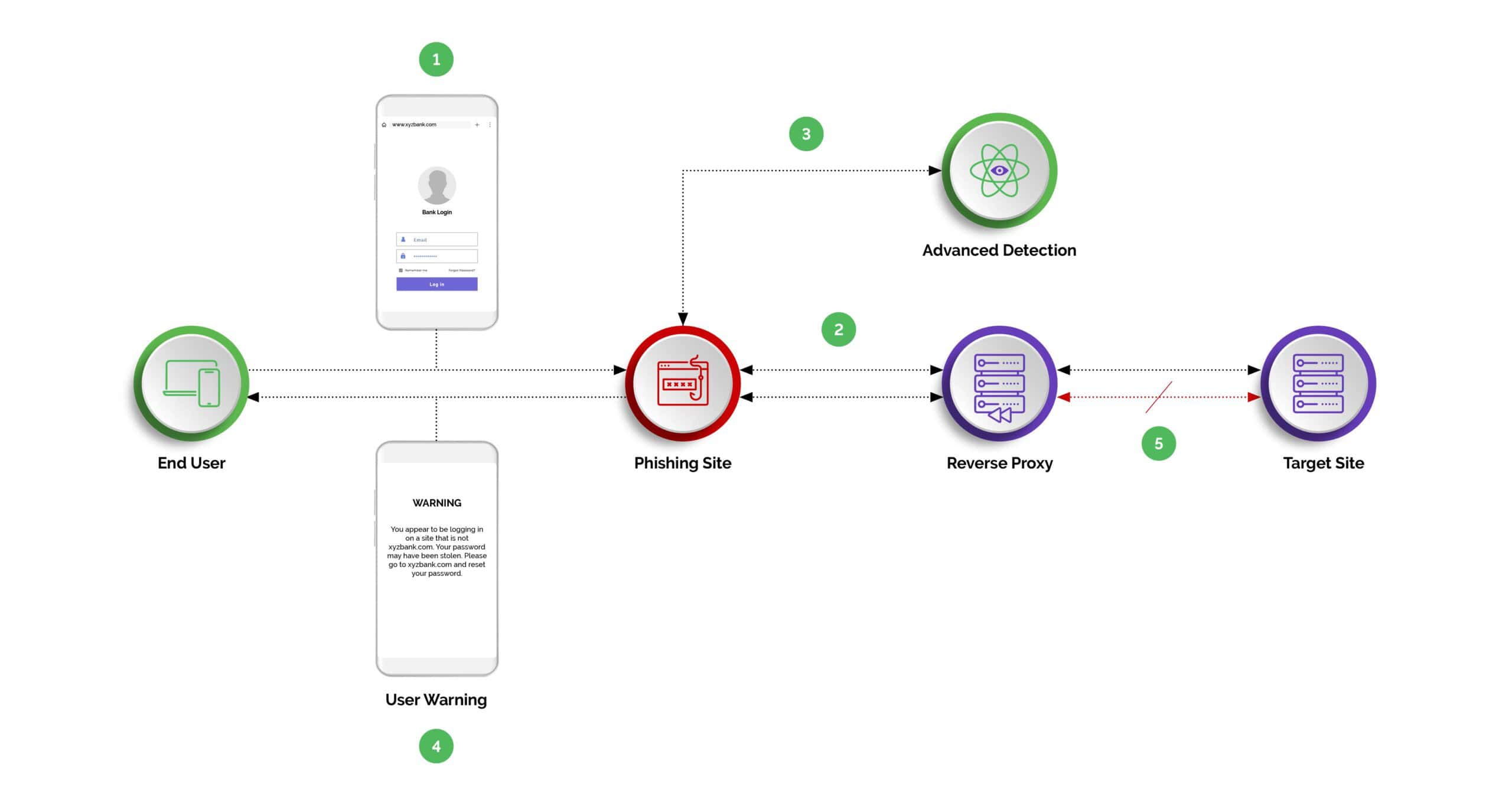
- Step One: The user is tricked into clicking on a malicious URL/link.
- Step Two: The phishing site is returned to the user, while the reverse proxy sniffs the traffic to the target site.
- Step Three: Arkose Phishing Protection identifies the phishing traffic, based on numerous signals.
- Step Four: Arkose Phishing Protection warns the user they are browsing a malicious copy of the target site. Alternatively, the target site may elect to simply monitor the suspicious hostname.
- Step Five: The login or registration fails, because the Arkose session token check fails.
The unique position of the Arkose Phishing Protection solution in the website's login/registration workflow, combined with its advanced phishing detection and challenge capabilities, makes it a potent defense mechanism against reverse-proxy-based MITM phishing attacks.
About Arkose Labs
Arkose Labs is the global leader in bot management and online account protection, which is why the world’s leading companies choose to partner with the firm to beat the adversary. Its mission is to create an online environment where all consumers are protected from malicious activity. And its foundational technology ensures it accomplishes the mission. Its AI-based platform combines powerful risk assessments with dynamic attack response that significantly increases the adversary’s effort to attack, which ultimately undermines the ROI behind those attacks. When financially-motivated attackers cannot make enough money attacking a company, they move on to less protected targets.
The company offers the world’s first and only $1 million credential stuffing warranty. Headquartered in San Mateo, CA with offices in Brisbane and Sydney, Australia, San Jose, Costa Rica, and London, UK, Arkose Labs debuted as the 83rd fastest-growing company in North America on the 2021 Deloitte Fast500 ranking.