What is bot management?
A large chunk of digital traffic today is composed of bots, which includes both good and malicious bots. With advanced capabilities, bots can easily scale up attacks to wreak havoc on digital businesses. It is, therefore, critical to detect and stop malicious bots before they can exploit business networks.
Bot management is a strategy that enables businesses to detect bot activity, identify its source and stop malicious bots while allowing good bots (such as search engine crawlers) to access their websites and apps. Software solutions that allow the mitigation of business risks emanating from bot-driven attacks are a key component of this strategy. Bot management is useful in fighting automated attacks such as credential stuffing, account takeover, new account fraud, scraping, scalping, and more.
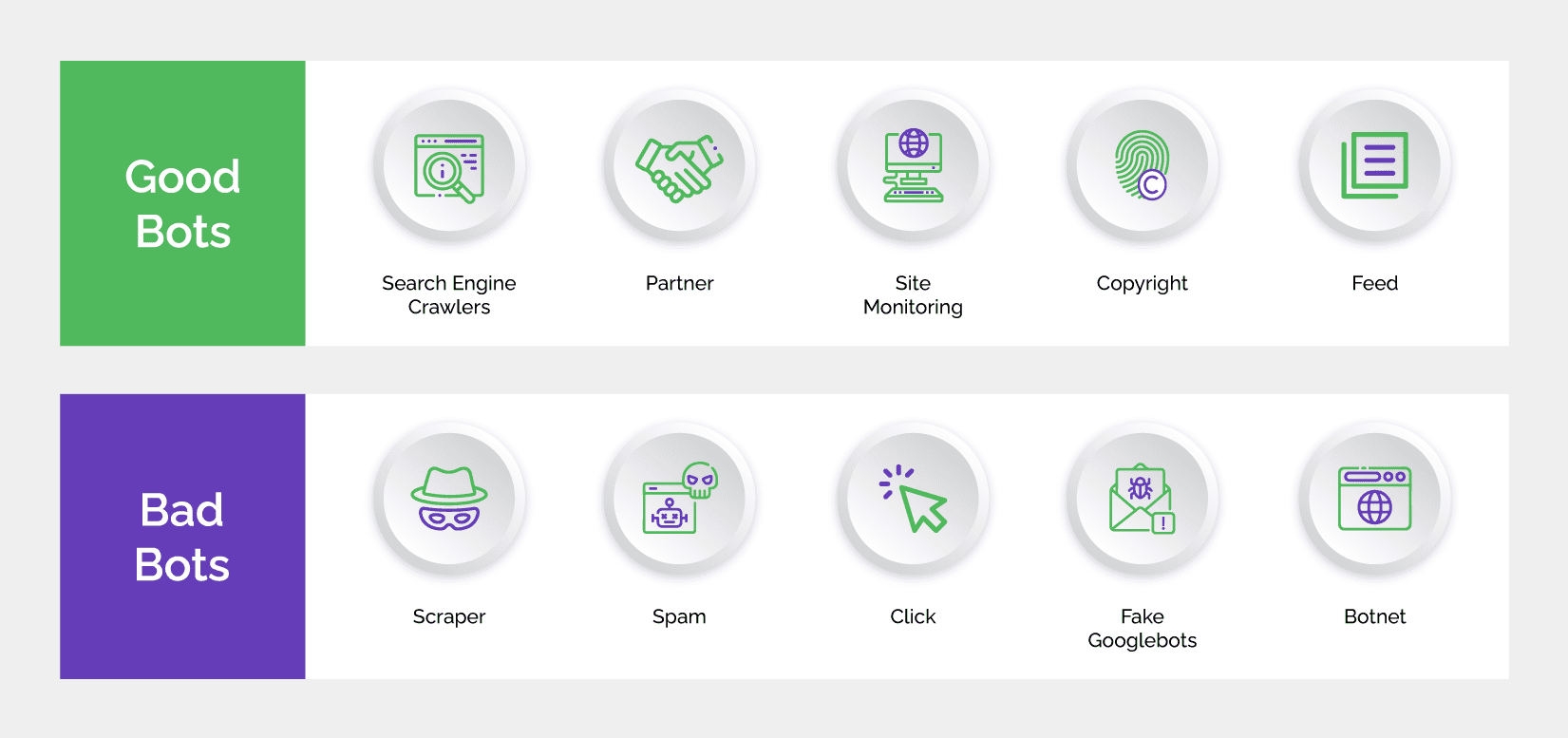
Over the years, a number of bot management solutions have been developed to help digital businesses filter out malicious bots. These solutions make use of multiple technologies including machine learning, artificial intelligence, and website development technologies.
Common bot threats
Attackers are in the business of making money. Naturally, they would want to maximize profits with the least possible investments. Since bots, with advanced capabilities, are available easily and cheaply, attackers rely heavily on them to launch mass-scale and complex attacks. Some of the common automated attacks that affect websites, apps, and APIs across industries are as mentioned below:
- Credential stuffing: Attackers use bots to match thousands of stolen username and password combinations to arrive at valid matches. They can choose to sell the databases of these valid credentials to third parties or refine the lists further – say according to industries or assets contained – to fetch more money. They can also use these valid credentials themselves to power account takeover attacks.
- Account takeover: Using valid username-password combinations, attacks hack into genuine user accounts and manipulate the compromised accounts at whim. Financial assets are just the first step at exploiting the compromised accounts, which can be used to redeem loyalty points, seek loans, phishing, disseminating spam, money laundering and a number of other downstream frauds.
- New account fraud: Fraudsters combine stolen consumer information with fake identity elements to create synthetic identities. Automation speeds up the new fake account creation process. Fraudsters use these fake accounts to pocket bonuses and freebies that many businesses offer to attract new customers. They are also used for money muling and opening new lines of credit. Fake accounts are also used to manipulate ratings and reviews on eCommerce and gaming platforms, phishing and disseminating spam.
- Password spraying: To validate a username and password combination, attackers use one password – usually the default password –across multiple accounts before trying out another password. These matched credentials are then used to fuel a number of attacks.
- Credit card testing: Attackers make small purchases on the stolen credit cards to test their validity. Since these transactions are small, they usually go unnoticed. However, fraudsters learn that the credit card is valid and use them for larger purchases.
- Scraping: Data is the lifeblood of any business and fraudsters too need data for monetization opportunities. Using bots, scripts and human click farms, attackers can extract large amounts of data from websites and apps rather quickly. They can sell the scraped data to third parties or on the dark web. When attackers sell scraped business-sensitive data such as pricing details to competitors, it can jeopardize the business strategy of the affected business. Fraudsters may also use this data themselves to launch several attacks as explained above.
- Phishing: Over the years, phishing has evolved into a preferred method for attackers to extract personal and sensitive user information. Automation can help scale up the attacks, increasing the risk for businesses manifold.
- Denial of service (DDoS): Attackers use botnets – and recently IoT devices as well – to spam servers and overwhelm business networks. This results in the attacked websites or applications becoming unavailable to users. These attacks are especially launched during online sales events to cause damage to businesses by forcing genuine customers to shop elsewhere.
How bot management works
Bot management solutions monitor the incoming digital traffic on a website, app, or an API to detect and block malicious activity. These solutions are a combination of several tools and technologies that help businesses to distinguish between malicious bots and good users. These include artificial intelligence, machine learning, data analytics, behavioral biometrics, device fingerprinting, and a host of other techniques.
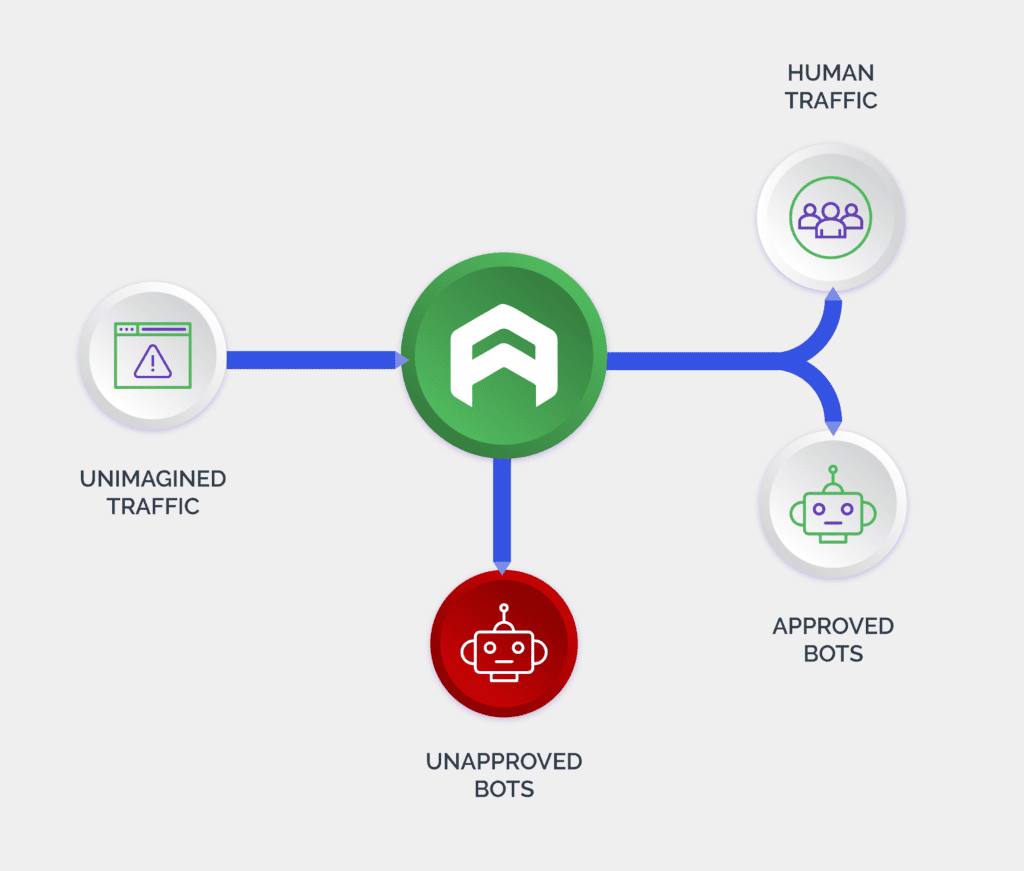
With an increase in the volume of digital interactions, malicious bot activity, too has risen. Furthermore, bots have acquired human-like capabilities, which allows them to interact with fraud solutions in a way a human would do. In an instance where more nuanced human interaction is required, these bots are intelligent enough to hand over the attack to human click farms. This makes it even more challenging for businesses to tell fraudsters from legitimate users.
Bot management solutions currently follow three approaches namely static, challenge-based, and behavioral to identify and stop bot-driven attacks. Depending on the level of threat they face, digital businesses use one or a combination of these approaches. They can also outsource bot management services to vendors that specialize in this area.
Importance of bot management
As mentioned before, a large chunk of digital traffic today comprises bots. Attackers are using advanced bots to launch a myriad of complex attacks at scale, which puts digital businesses as well as their consumers at risk. Not only do businesses face financial losses trying to restore user accounts, remediating the attacks and paying penalties due to non-compliance, they also suffer damage to brand equity. It takes years of effort to build reputation and customer trust that can get eroded in no time. In worst cases, loss of customers and revenue can result in the business shutting down.
Affected consumers may suffer damage to their credit scores that can hamper their ability to seek credit in future. They may end up repaying loans they never solicited and worse, they may be punished for a criminal activity executed from their compromised accounts. It may take a toll on their mental wellbeing trying to get their digital identity restored, which may never happen.
Bot management is, therefore, critical for business continuity and safeguarding business and consumer interests from the damaging consequences of a cyberattack. Digital businesses would do well to prioritize bot management as an integral part of their overall fraud defense system.
Limitations of current bot management solutions
Bot management solutions have an important role to play in the fight against automated attacks. However, blocking users on a slight suspicion or lowering the guards for the purpose of customer acquisition can be counterproductive. Extremely stringent authentication can introduce unnecessary friction and cause consumer discontent. Whereas, lenient authentication can open the gates for attackers to rush in.
Evolving consumer behavior, manipulation of digital identities, and rising bot sophistication have blurred the distinction between malicious and legitimate users. Data-driven bot management solutions that look for clear trust or mistrust signals cannot effectively tell a malicious bot from a good user.
To make matters worse for digital businesses, bot management solutions such as CAPTCHAs have lost their supremacy over bots. While bots have become sophisticated using advanced technologies, CAPTCHAs have not been able to evolve at the same pace. This has resulted in CAPTCHAs being cleared by even some of the basic bots.
A zero-tolerance approach
Digital businesses cannot keep absorbing fraud losses as a cost of doing business. This only acts as an incentive for attackers to continue making money. The stakes are high and digital businesses need a fresh approach to bot management – an approach that ensures long-term protection from bots of various levels of advancement.
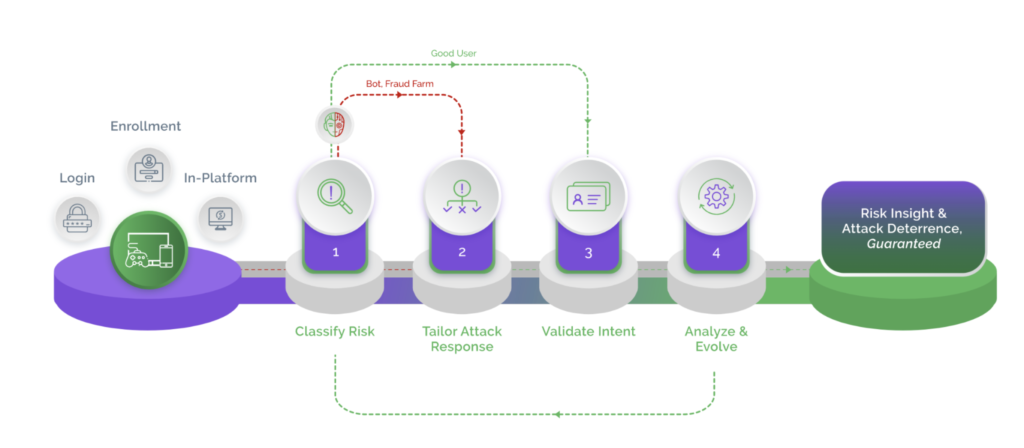
Point solutions and data-driven solutions are proving inadequate, exposing businesses and consumers to an elevated risk of cyberattacks. It is time now for businesses to adopt a zero-tolerance approach that focuses on deterrence rather than remediation. Arkose Labs uses targeted friction to fight bots and offers a 100% SLA on the elimination of automated attacks. Arkose Labs’ zero-tolerance approach also forces malicious humans to abandon the attacks without compromising on user experience.